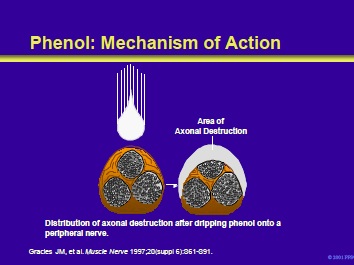
Phenol (carbolic acid) is a major oxidized metabolite of benzene. Phenol is a potent proteolytic agent. Concentrations of phenol of 5% to 7% are proteolytic and dissolve tissues on contact.
When injected immediately adjacent to a nerve, phenol in high concentrations produces a chemical neurolysis. These effects are nonselective across nerve fiber size and are most prominent on the nerve’s outer aspect. Following an injection of a neurolytic dose of phenol, local anesthetic effects are observed within 5 to 10 minutes.
After 24 hours, the long-term effects of neurolysis on the manifestations of spasticity occur. The duration of these effects may be related to the length of the nerve segment denervated. They have an average duration of 6 months but can last as long as a year.
Gracies JM, Elovic E, McGuire J, et al. Traditional pharmacological treatments for spasticity part I: local treatments. Muscle Nerve 1997;20(suppl 6):S61-S91.
Article Index
Page 4 of 11
Add comment