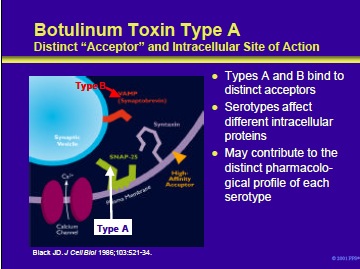
This slide shows an expanded view of a nerve terminal, depicting an extracellular acceptor and some of the intracellular proteins affected by the various botulinum neurotoxin serotypes. Botulinum toxin serotypes A and B bind to distinct acceptors on the external membrane of cholinergic neurons. These are the only two serotypes for which the acceptors have been well studied.
Once inside the nerve terminal, botulinum neurotoxins act by cleaving one or more of the intracellular proteins needed for neurotransmitter release. • Botulinum neurotoxin types A, C1 and E each cleave SNAP-25 at different sites •
Botulinum toxin types B, D, F, and G each cleave VAMP (synaptobrevin) at different sites • Type C1 also cleaves the protein syntaxin It is likely that these differences contribute to the distinct pharmacological profiles of the various serotypes (detailed in subsequent slides).
Black JD, Dolly JO. Interaction of 125-I labeled botulinum neurotoxins with nerve terminals. I. Ultrastructural autoradiographic localization and quantitation of distinct membrane acceptors for types A and B on motor nerves. J Cell Biol 1986;103:521-34.
Article Index
Page 2 of 16
Add comment