Page 9 of 18
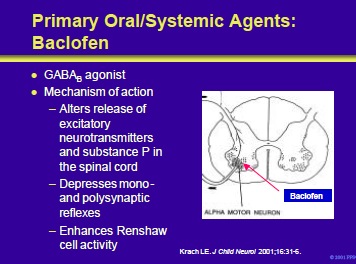
Baclofen is a structural analog of GABA. It appears to be at the level of the spinal cord by binding to GABAB receptors and blocking polysynaptic and monosynaptic afferents. Its mechanism of action may be as a direct inhibitory neurotransmitter or the result of hyperpolarization of afferent nerve terminals.
Krach LE. Pharmacotherapy of spasticity: oral medications and intrathecal baclofen. J Child Neurol 2001;16:31-6.
Add comment