- Lectures / Webinars
- 3. Treatment of Patients with cerebral palsy and spasticity
3. Treatment of Patients with cerebral palsy and spasticity
HotTreatment of Patients with Cerebral Palsy and Spasticity
The following sections expand upon the various treatment options in patients with spasticity secondary to cerebral palsy.
They include:
- Pharmacotherapy
- Surgical therapy
- Rehabilitation

Therapeutic approaches to the patient with cerebral palsy and spasticity include the following:
- Pharmacotherapy
- Surgical interventions
- Rehabilitation
The goals of these interventions include:
- Decreasing spasticity
- Decreasing the pain associated with spasticity
- Preventing, decreasing the incidence, or reversing contractures
- Facilitating rehabilitation and care
- Improving functional ability and independence
- Improving ambulation and/or mobility
- Improving quality of life
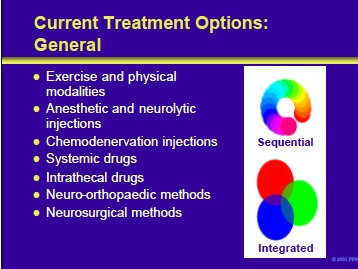
Current Treatment Options: General
Current treatment options in the patient with spasticity include:
- Physical therapy
- Oral/systemic agents
- Nerve blocks
- Botulinum neurotoxin type A (BTX-A)
- Intrathecal baclofen
- Neuro-orthopaedic interventions
- Neurosurgical interventions
In most instances, the child’s interests are best served by an approach that integrates these various options rather than relying on a sequential approach.

Optimum treatment of the child with spasticity requires an integrated, rather than a hierarchical, approach. For example, serial casting can be facilitated by BTX injections at the same time that the child is receiving oral antispasticity medications.
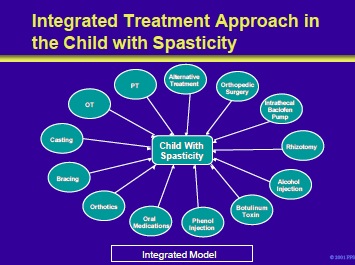
This slide illustrates the integrated approach to the child with spasticity. The child is the center of a variety of therapeutic interventions designed to maximize function and quality of life.
- GO TO NEXT SECTION : Management of spasticity in cerebral palsy Part IV - Rehabilitation Management
Add comment