Page 269 - ILAE_Lectures_2015
P. 269
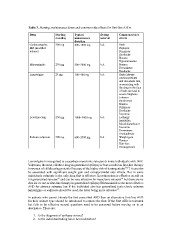
Table 3. Starting, maintenance doses and common side effects for first-line AEDs.
Drug Starting Typical Dosing Commonest side
dose/day maintenance interval effects
Carbamazepine dose/day b.d.
MR (modified 200 mg b.d. Rash
release) 4001800 mg b.d. Diplopia
Dizziness
Ethosuximide 250 mg 5002000 mg b.d. Headache
Lamotrigine 25 mg 100400 mg b.d. Nausea
Hyponatraemia
Levetiracetam 250 mg 10003000 mg Nausea
Drowsiness
Sodium valproate 300 mg 6002500 mg Headache
Rash (always
caution patients
and document this,
as persisting with
the drug in the face
of rash can lead to
severe Stephens
Johnson
Syndrome)
Nausea
Dizziness
Headache
Insomnia
Lethargy
Irritability
Mood disturbance
Insomnia
Drowsiness
Unsteadiness
Weight gain
Tremor
Hair loss
Teratogenesis
Lamotrigine is recognised to exacerbate myoclonic seizures in some individuals with JME.
Valproate, the most effective drug in generalised epilepsy is best avoided as first-line therapy
in women of childbearing potential because of the higher risk of teratogenicity13,14; it can also
be associated with significant weight gain and extrapyramidal side effects. But in some
individuals valproate is the only drug that is effective. Levetiracetam is effective as add-on
for generalised seizures15 and can be very effective for myoclonic seizures16 but there are no
data for its use as first-line therapy in generalised epilepsy Ethosuximide is the most effective
AED for absence seizures, but if the individual also has generalised tonic-clonic seizures
lamotrigine or valproate should be used, the latter being more effective17.
In patients who cannot tolerate the first prescribed AED then an alternative first-line AED
for their seizure type should be introduced to replace the first. If the first AED is tolerated
but fails to be effective several questions need to be answered before moving on to an
alternative. These are:
1. Is the diagnosis of epilepsy correct?
2. Is the individual taking his or her medication?