Clinical Spectrum And Genetic Variations Of Rett Syndrome Experienced From The Child Neurodevelopmental Centre Of A Tert
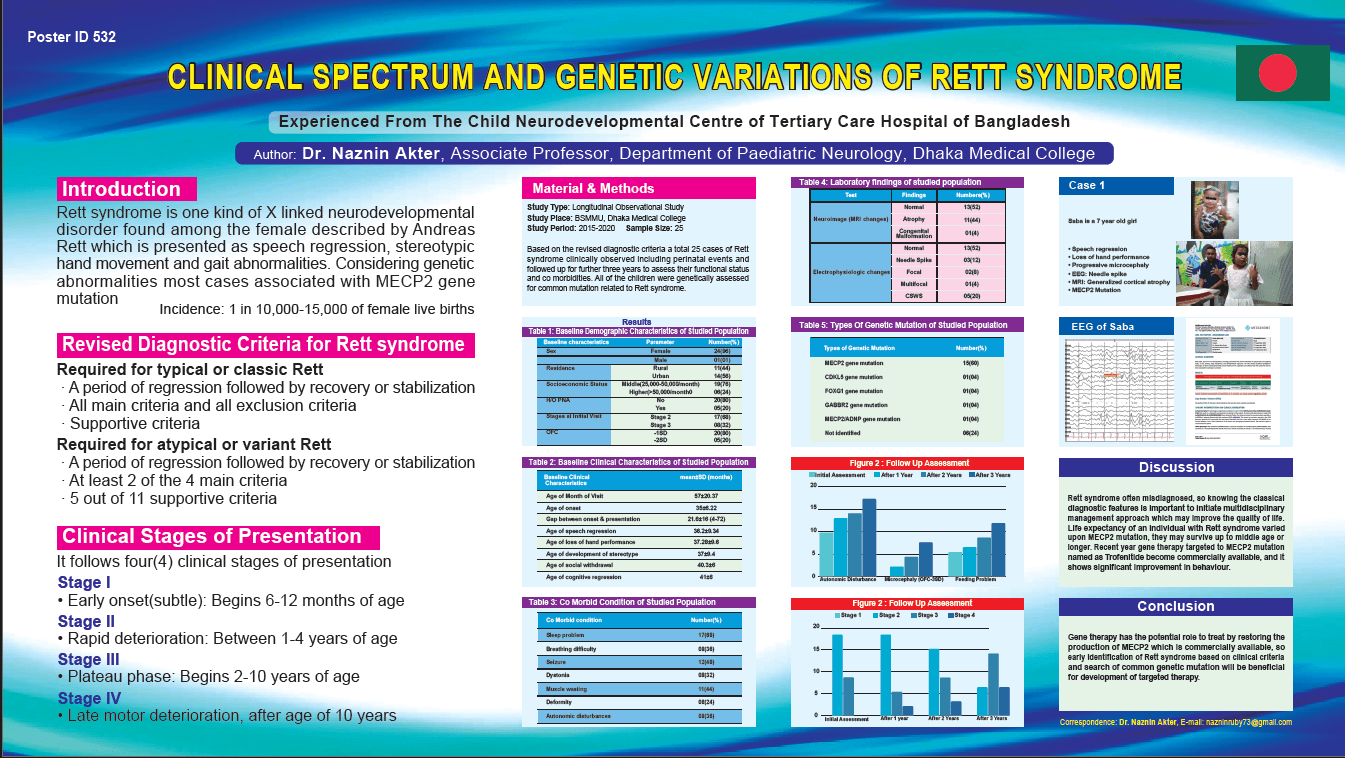
Background: Rett syndrome is one kind of X linked neurodevelopmental disorder found among the female described by Andreas Rett which is presented as speech regression, stereotypic hand movement and gait abnormalities. Considering genetic abnormalities most cases associated with MECP2 gene mutation Materials & methods: Based on the diagnostic criteria a total 25 cases of Rett syndrome clinically observed including perinatal events and followed up for further three years to assess their functional status and co morbidities. All of the children were genetically assessed for common mutation related to Rett syndrome. Results: All studied children had no perinatal complications, only six (6) we found progressive microcephaly, all (100%) had neurodevelopmental regression on speech, cognition, social and fine motor domain. Epilepsy (45%), sleep disorder (75%) and respiratory distress (37.5%) was the common co morbid condition. At the final assessment four of them were bounded to wheel chair. Pathogenic genetic mutation in the X-linked gene encoding methyl-CpG-binding proten-2 (MECP2) were present among fifteen (15) children, CDKL5, FOXG1 and GABBR2 gene mutation was found one from each group, only one male child have association with ADNP gene mutation, no genetic mutation were identified from 6 children with clinical Rett. Conclusion: Gene therapy has the potential role to treat by restoring the production of MECP2 so early identification of common genetic mutation of Rett syndrome will be beneficial for development of targeted therapy.
Naznin Ruby
Dhaka Medical College
Bangladesh
Naznin Ruby
Dhaka Medical College
Bangladesh