Assessment Of Functional Connectivity Patterns In Children With Epilepsy With Myoclonic-Atonic Seizures
Introduction
Epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures (EMAtS) (Doose syndrome) is a rare developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Seizures remit in 60% but others enter a Stormy Phase (SP) of worsening seizures and recurrent non-convulsive status epilepticus. Our study aimed to distinguish the functional connectivity patterns among electroencephalographs (EEGs) of children diagnosed with a) SP, b) Lennox Gastaut Syndrome (LGS), c) non-SP EMAtS and d) normal EEGs in children without epilepsy.
Methods
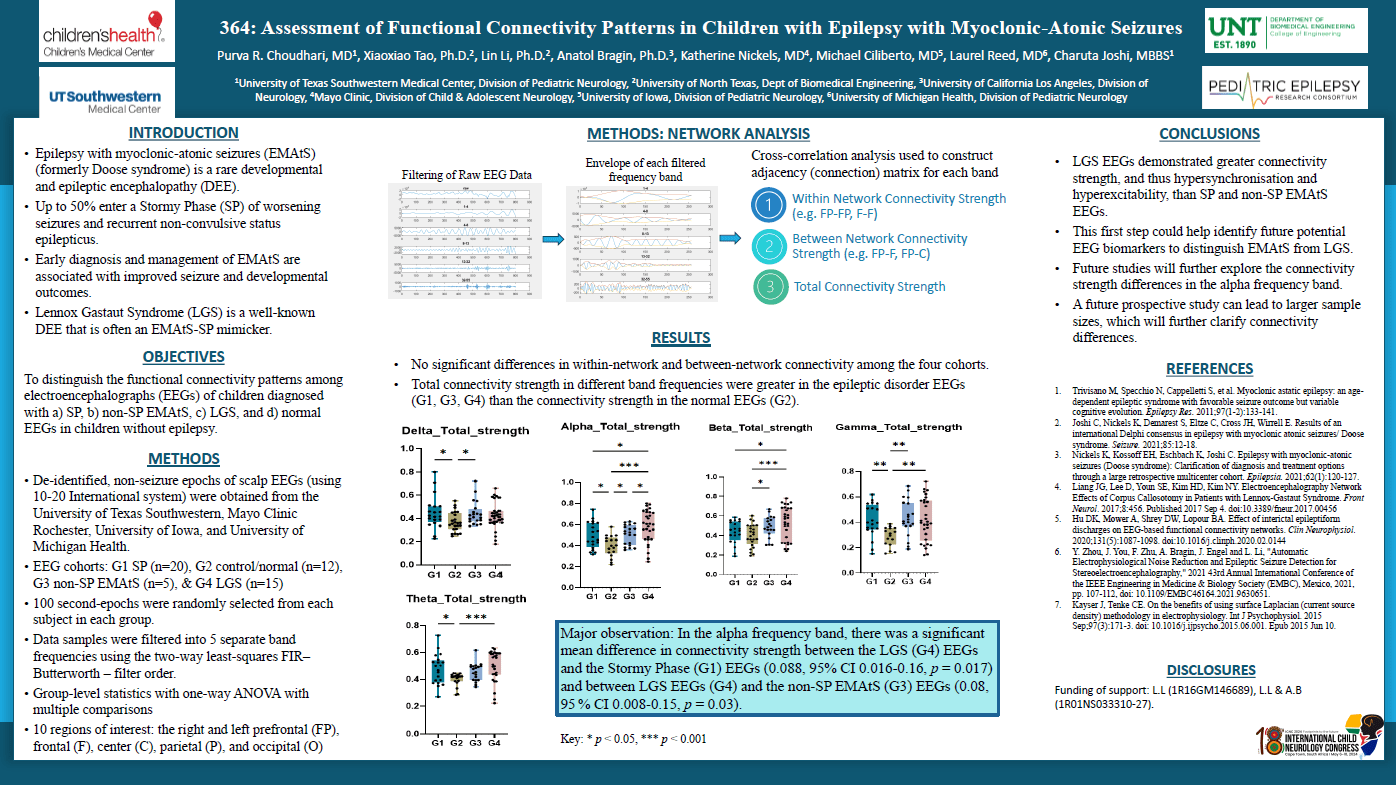
We analyzed non-seizure epochs from scalp EEGs of patients from four groups: SP (n=20), non SP EMAtS (n=5), LGS (n=15), and non-epilepsy group (n=12). EEG data was pre-processed through a pipeline including automatic motion artifact rejection and independent component analysis for cleaning. Ten regions of interest were selected: the right and left prefrontal, frontal, center, parietal and occipital regions. Functional connectivity was analyzed using coherence coupling from 1-20 Hz and 3-70 Hz.
Results
Total connectivity strength (CS) was greater among SP (CS 0.37 ± 0.089) and LGS (CS 0.418 ± 0.089) EEGs, indicating greater hyperexcitability in these groups (Figure 1). Normal EEGs demonstrated the lowest CS among all groups. CS in the LGS group was significantly greater than the normal EEG group (p = 0.02).
Conclusion
SP and LGS EEGs demonstrated greater CS, and thus hyperexcitability, which is consistent with the clinical phenotypes of the SP and LGS. Further evaluation will include analysis of connectivity within brain regions and cross-region for each group. This first step will help identify future potential EEG biomarkers and predictors for SP in children with EMAtS.
Purva Choudhari
University of Texas Southwestern
United States
Xiaoxiao Tao
University of North Texas
United States
Lin Li
University of North Texas
United States
Anatol Bragin
University of California, Los Angeles
United States
Katherine Nickels
Mayo Clinic
United States
Michael Ciliberto
University of Iowa
United States
Laurel Reed
University of Michigan Health
United States
Charuta Joshi
University of Texas Southwestern
United States