Page 35 - ILAE_Lectures_2015
P. 35
results in greatly improved seizure control and these lesions tend not to recur103,105 although there
are rare reports of malignant transformation106. DNT tend to lack the typical 1p/19q deletions
seen in oligodendrogliomas and IDH1 mutations associated with more conventional low-grade
gliomas and astrocytomas107.
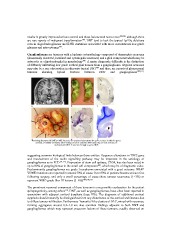
Gangliogliomas are tumours with a biphasic cytopathology composed of dysmorphic neurones
(abnormally clustered, localised and cytomegalic neurones) and a glial component which may be
astrocytic or oligodendroglial in morphology108. A major diagnostic difficulty is the distinction
of diffusely infiltrating low-grade cortical glial tumour from a ganglioglioma. Atypical neurones
may also be a rare observation in otherwise typical DNT103 and there are reports of glioneuronal
tumours showing hybrid features between DNT and ganglioglioma109,110.
suggesting common biological links between these entities. Sequence alterations in TSC2 gene
and involvement of the reelin signalling pathway may be important in the aetiology of
gangliogliomas as in FCD111,112. Expression of stem cell epitope, CD34, has also been noted in
up to 80% of gangliogliomas in the small cell component108, which may be of diagnostic value.
Predominantly gangliogliomas are grade I neoplasms associated with a good outcome. BRAF
V600E mutations are reported in around 50% of cases. Over 80% of patients become seizure free
following surgery, and only a small percentage of cases show tumour recurrence (13%) or
represent WHO grade II or III lesions (26%)104,108,113.
The prominent neuronal component of these tumours is one possible explanation for the potent
epileptogenicity, among others114. DNT, as well as gangliogliomas, have often been reported in
association with adjacent cortical dysplasia (type IIIb). The diagnosis of additional cortical
dysplasia should naturally be distinguished from any disturbance of the cortical architecture due
to diffuse tumour infiltration. Furthermore ‘hamartia’-like clusters of OLC, mixed with neurones,
forming aggregates around 0.21.0 are also common findings adjacent to both DNT and
gangliogliomas which may represent precursor lesions of these tumours, readily observed on