Page 253 - ILAE_Lectures_2015
P. 253
change, with Kayser Fleischer rings on the iris. Extrapyramidal features, in particular in
association with non-epileptic drop attacks (cataplexy) may suggest Niemann Pick type C.
The progressive myoclonic epilepsies are again likely to present with infrequent seizures,
with a later increase in frequency and associated cognitive concerns. A high index of
suspicion is required to investigate these early.
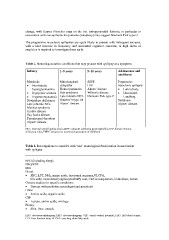
Table 1. Neurodegenerative conditions that may present with epilepsy as a symptom.
Infancy 15 years 510 years Adolescence and
adulthood
Metabolic Mitochondrial SSPE Progressive
cytopathy HIV myoclonic epilepsy
Non-ketotic Homocysteinuria Alpers’ disease
hyperglycinaemia Rett syndrome Wilson’s disease Lafora body
Late infantile NCL Niemann Pick type C
D-glyceric aciduria Gaucher’s type III Unverricht-
Alpers’ disease Lundberg
Hyperammonaemia
Biotinidase deficiency Sialidoses
Late infantile NCL Alpers’ disease
Menkes syndrome
Krabbe disease
Tay Sachs disease
Peroxisomal disorders
Alpers’ disease
NCL: neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis; SSPE: subacute sclerosing panencephalitis; HIV: human immuno-
deficiency virus; PNDC: progressive neuronal degeneration of childhood
Table 2. Investigations to consider with ‘true’ neurological deterioration in association
with epilepsy.
EEG (including sleep)
ERG/VEP
MRI
Blood
FBC, LFT, NH3, amino acids, lysosomal enzymes,VLCFA,
bile salts, vacuolated lymphocytes/buffy coat, Cu/Caeruloplasmin, biotinidase, lactate
Genetic studies for specific conditions
Discuss with paediatric neurologist and geneticist
Urine
Amino acids, organic acids
CSF
Lactate, amino acids, virology
Biopsy
Skin, liver, muscle
EEG: electroencephalogram; ERG: electroretinogram; VEP: visual evoked potential; FBC: full blood counts;
LFT: liver function tests; VLCFA: very long chain fatty acids