Anti-Hu associated encephalitis as the initial presentation of neuroblastoma
Seda Kanmaz, Sanem Yilmaz, Eda Ataseven, Dilara Ece Toprak, Tugce Ince, Hepsen Mine Serin, Mehmet Kantar, Hasan Tekgul
Introduction: The most common cause of anti-Hu-associated encephalitis, which is extremely rare in childhood, is the recurrence of neuroblastoma.
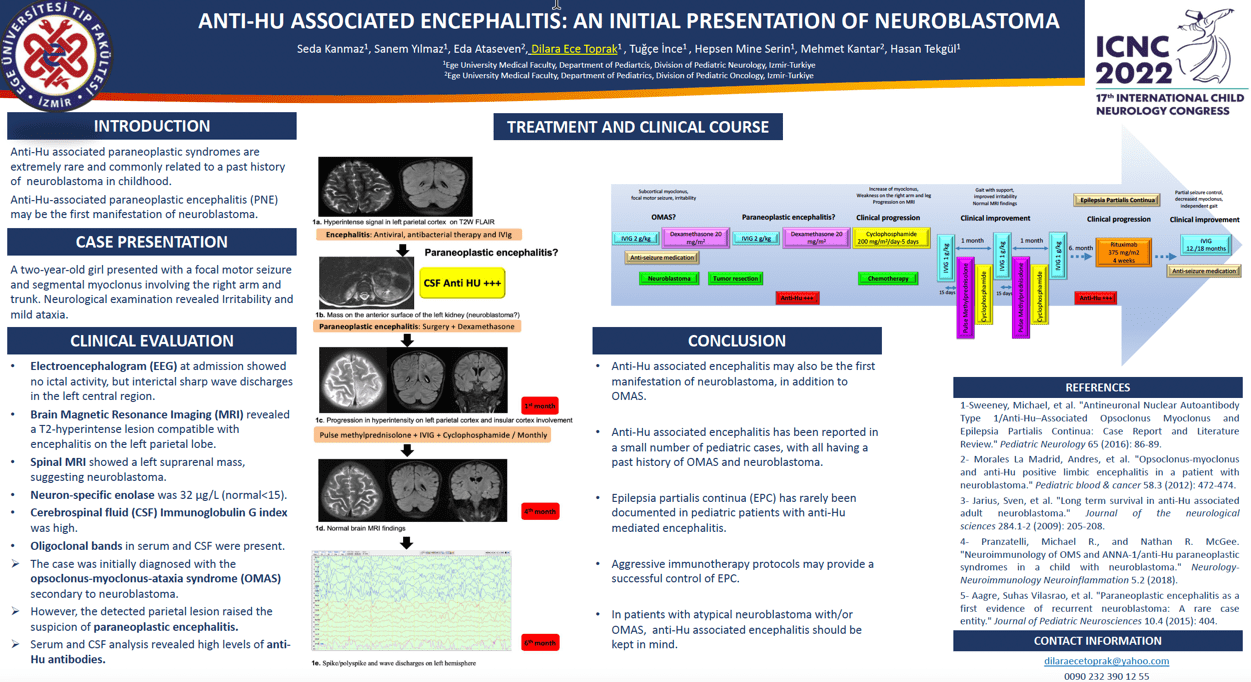
Case: A two-year-old girl presented with a focal motor seizure and segmental myoclonus involving the right arm and trunk. Brain MRI revealed T2-hyperintense lesion compatible with encephalitis on the left parietal lobe. Spinal MRI incidentally showed a left suprarenal mass, suggesting neuroblastoma. NSE was 32 µg/L (normal<15). The case was initially diagnosed with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome (OMS) secondary to neuroblastoma. However, the detected parietal lesion raised the suspicion for anti-Hu encephalitis and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis revealed high levels of anti-Hu antibody. The patient underwent surgery and the histopathology confirmed neuroblastoma. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) and dexamethasone was initiated. Since the first month cranial MRI revealed progression, besides the chemotherapy regimen including cyclophosphamide, monthly IVIg and pulse methylprednisolone were administered. At the sixth month of therapy, myoclonic movements gradually increased and became continuous. The ictal video EEG recordings of the case led to the diagnosis of epilepsia partialis continua. Due to the clinical picture worsening despite steroids, IVIg and cyclophosphamide, the anti-Hu antibody level in CSF was reassessed and was found to remain high. Rituximab therapy was initiated with partial response. The clinical course of the patient is summarized in the Figure 1a-e.
Conclusion: The case presented here is the first known case demonstrating that the initial clinical presentation of neuroblastoma may be anti-Hu encephalitis.
Keywords: Neuroblastoma, anti-Hu, encephalitis
Seda Kanmaz
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Sanem Yilmaz
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Eda Ataseven
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Dilara Ece Toprak
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Tugce Ince
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Hepsen Mine Serin
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Mehmet Kantar
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Hasan Tekgul
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Introduction: The most common cause of anti-Hu-associated encephalitis, which is extremely rare in childhood, is the recurrence of neuroblastoma.
Case: A two-year-old girl presented with a focal motor seizure and segmental myoclonus involving the right arm and trunk. Brain MRI revealed T2-hyperintense lesion compatible with encephalitis on the left parietal lobe. Spinal MRI incidentally showed a left suprarenal mass, suggesting neuroblastoma. NSE was 32 µg/L (normal<15). The case was initially diagnosed with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome (OMS) secondary to neuroblastoma. However, the detected parietal lesion raised the suspicion for anti-Hu encephalitis and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis revealed high levels of anti-Hu antibody. The patient underwent surgery and the histopathology confirmed neuroblastoma. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) and dexamethasone was initiated. Since the first month cranial MRI revealed progression, besides the chemotherapy regimen including cyclophosphamide, monthly IVIg and pulse methylprednisolone were administered. At the sixth month of therapy, myoclonic movements gradually increased and became continuous. The ictal video EEG recordings of the case led to the diagnosis of epilepsia partialis continua. Due to the clinical picture worsening despite steroids, IVIg and cyclophosphamide, the anti-Hu antibody level in CSF was reassessed and was found to remain high. Rituximab therapy was initiated with partial response. The clinical course of the patient is summarized in the Figure 1a-e.
Conclusion: The case presented here is the first known case demonstrating that the initial clinical presentation of neuroblastoma may be anti-Hu encephalitis.
Keywords: Neuroblastoma, anti-Hu, encephalitis
Seda Kanmaz
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Sanem Yilmaz
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Eda Ataseven
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Dilara Ece Toprak
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Tugce Ince
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Hepsen Mine Serin
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Mehmet Kantar
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Hasan Tekgul
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey