A case of TUBGCP2-associated tubulinopathy with a novel missense variant
Yavuz Sayar, Miraç Yıldırım, Ömer Bektaş, Çiğdem İlter Uçar, Serap Teber
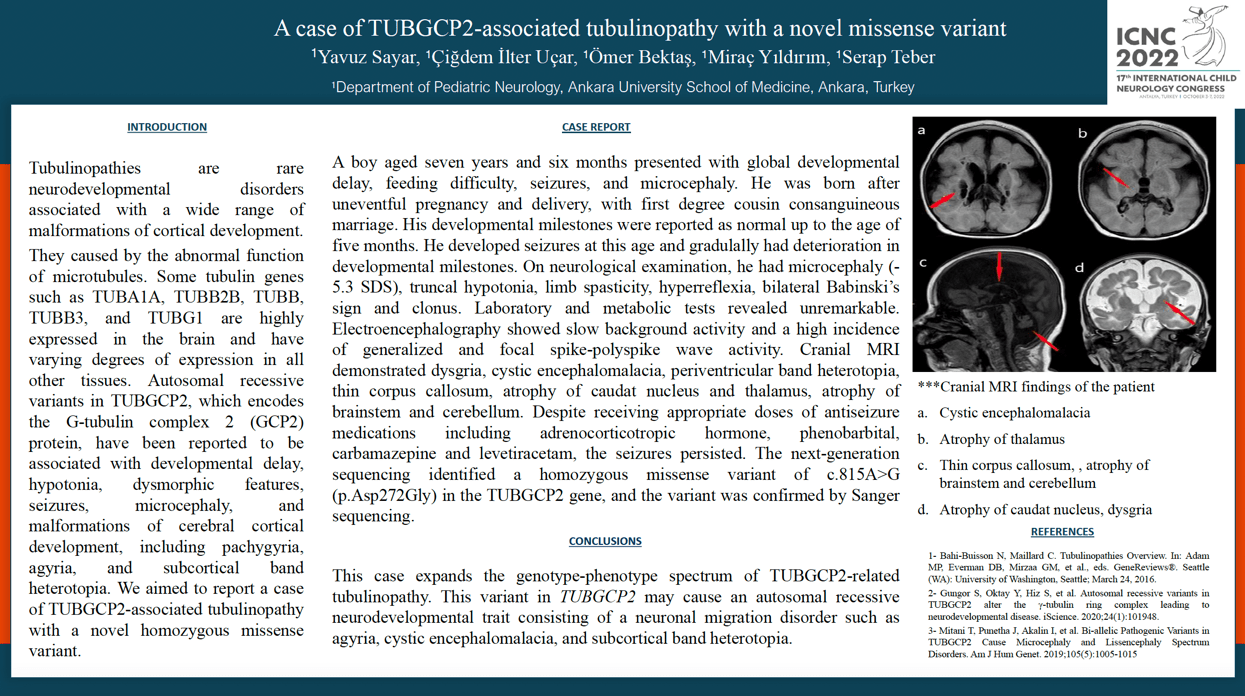
Objectives: Tubulinopathies are rare neurodevelopmental disorders associated with a wide range of malformations of cortical development. We aimed to report a case of TUBGCP2-associated tubulinopathy with a novel homozygous missense variant. Case Presentation: A boy aged seven years and six months presented with global developmental delay, feeding difficulty, seizures, and microcephaly. He was born after uneventful pregnancy and delivery, with first degree cousin consanguineous marriage. His developmental milestones were reported as normal up to the age of five months. He developed seizures at this age and gradulally had deterioration in developmental milestones. On neurological examination, he had microcephaly (-5.3 SDS), truncal hypotonia, limb spasticity, hyperreflexia, bilateral Babinski sign and clonus. Laboratory tests and metabolic tests revealed unremarkable. Electroencephalography showed slow background activity and a high incidence of generalized and focal spike-polyspike wave activity. Cranial MRI demonstrated dysgria, cystic encephalomalacia, periventricular band heterotopia, thin corpus callosum, atrophy of caudat nucleus and thalamus, atrophy of brainstem and cerebellum. Despite receiving appropriate doses of antiseizure medications including adrenocorticotropic hormone, phenobarbital, carbamazepine and levetiracetam, the seizures persisted. The next-generation sequencing identified a homozygous missense variant of c.815A>G (p.Asp272Gly) in the TUBGCP2 gene, and the variant was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Conclusion: This case expands the genotype-phenotype spectrum of TUBGCP2-related tubulinopathy.
Keywords: Dysgria, novel variant, TUBGCP2, tubulinopathy
Yavuz Sayar
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Miraç Yıldırım
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Ömer Bektaş
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Çiğdem İlter Uçar
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Serap Teber
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Objectives: Tubulinopathies are rare neurodevelopmental disorders associated with a wide range of malformations of cortical development. We aimed to report a case of TUBGCP2-associated tubulinopathy with a novel homozygous missense variant. Case Presentation: A boy aged seven years and six months presented with global developmental delay, feeding difficulty, seizures, and microcephaly. He was born after uneventful pregnancy and delivery, with first degree cousin consanguineous marriage. His developmental milestones were reported as normal up to the age of five months. He developed seizures at this age and gradulally had deterioration in developmental milestones. On neurological examination, he had microcephaly (-5.3 SDS), truncal hypotonia, limb spasticity, hyperreflexia, bilateral Babinski sign and clonus. Laboratory tests and metabolic tests revealed unremarkable. Electroencephalography showed slow background activity and a high incidence of generalized and focal spike-polyspike wave activity. Cranial MRI demonstrated dysgria, cystic encephalomalacia, periventricular band heterotopia, thin corpus callosum, atrophy of caudat nucleus and thalamus, atrophy of brainstem and cerebellum. Despite receiving appropriate doses of antiseizure medications including adrenocorticotropic hormone, phenobarbital, carbamazepine and levetiracetam, the seizures persisted. The next-generation sequencing identified a homozygous missense variant of c.815A>G (p.Asp272Gly) in the TUBGCP2 gene, and the variant was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Conclusion: This case expands the genotype-phenotype spectrum of TUBGCP2-related tubulinopathy.
Keywords: Dysgria, novel variant, TUBGCP2, tubulinopathy
Yavuz Sayar
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Miraç Yıldırım
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Ömer Bektaş
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Çiğdem İlter Uçar
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Serap Teber
Ankara University School of Medicine
Turkey
Yavuz Sayar
Ankara University School of Medicine Turkey
Ankara University School of Medicine Turkey