PERONEAL NERVE PALSY DUE TO OSTEOCHONDROMA OF THE FİBULAR HEAD: A RARE CAUSE OF FOOT DROP
Recep Kamil Kilic, Salih Akbas, Akif Muhtar Ozturk, Ercan Demir
Objective:Peroneal nerve lesion is the most common cause of foot drop. Peroneal neuropathies often develop after trauma, direct injury or upon entrapment along the nerve proximal or distal to the fibular head. Peroneal nerve is rarely entrapped by osteochondroma in the fibular head, resulting in drop foot.
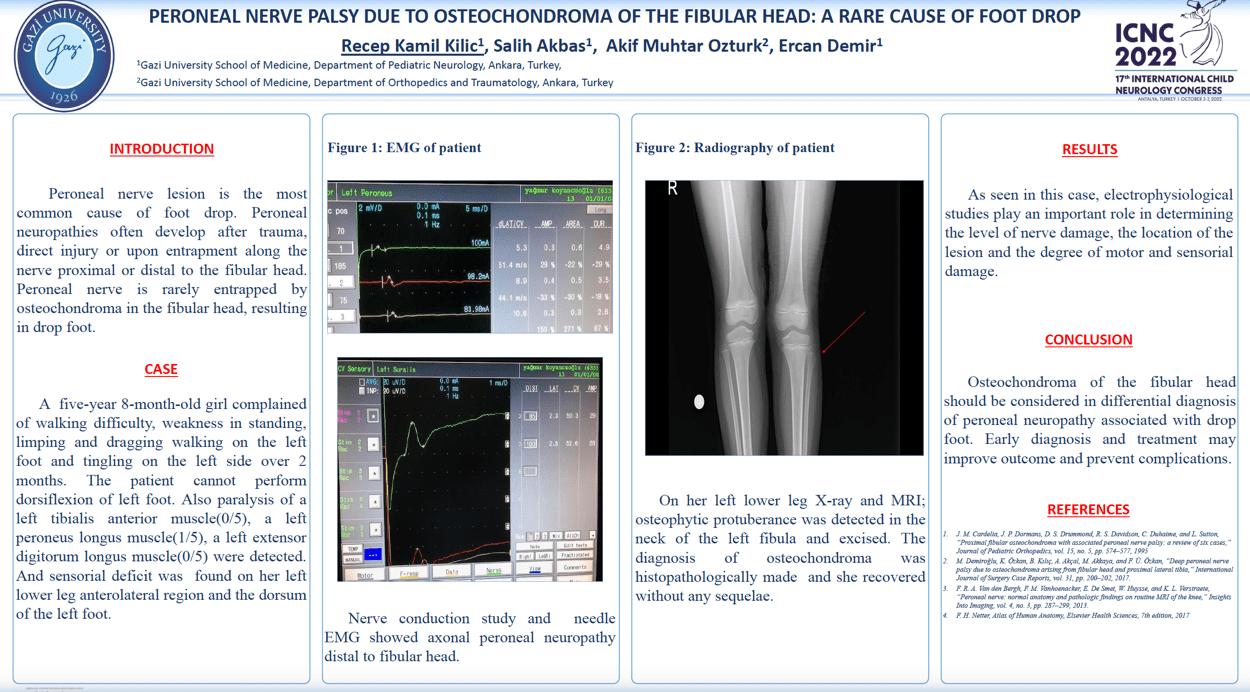
Methods:A five-year 8-month-old girl complained of walking difficulty,weakness in standing, limping and dragging walking on the left foot and tingling on the left side over 2 months.The patient cannot perform dorsiflexion of left foot. Also paralysis of a left tibialis anterior muscle(0/5), a left peroneus longus muscle(1/5), a left extensor digitorum longus muscle(0/5) were detected. And sensorial deficit was found on her left lower leg anterolateral region and the dorsum of the left foot. Nerve conduction study and needle EMG showed axonal peroneal neuropathy distal to fibular head. On her left lower leg X-ray and MRI;osteophytic protuberance was detected in the neck of the left fibula and excised. The diagnosis of osteochondroma was histopathologically made and she recovered without any sequelae.
Results: As seen in this case, electrophysiological studies play an important role in determining the level of nerve damage, the location of the lesion and the degree of motor and sensorial damage.
Conclusion: Osteochondroma of the fibular head should be considered in differential diagnosis of peroneal neuropathy associated with drop foot. Early diagnosis and treatment may improve outcome and prevent complications.
Keywords: Drop foot; Electromyography; Osteochondroma; Child; Peroneal nerve entrapment
Recep Kamil Kilic
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Salih Akbas
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Akif Muhtar Ozturk
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Ercan Demir
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Objective:Peroneal nerve lesion is the most common cause of foot drop. Peroneal neuropathies often develop after trauma, direct injury or upon entrapment along the nerve proximal or distal to the fibular head. Peroneal nerve is rarely entrapped by osteochondroma in the fibular head, resulting in drop foot.
Methods:A five-year 8-month-old girl complained of walking difficulty,weakness in standing, limping and dragging walking on the left foot and tingling on the left side over 2 months.The patient cannot perform dorsiflexion of left foot. Also paralysis of a left tibialis anterior muscle(0/5), a left peroneus longus muscle(1/5), a left extensor digitorum longus muscle(0/5) were detected. And sensorial deficit was found on her left lower leg anterolateral region and the dorsum of the left foot. Nerve conduction study and needle EMG showed axonal peroneal neuropathy distal to fibular head. On her left lower leg X-ray and MRI;osteophytic protuberance was detected in the neck of the left fibula and excised. The diagnosis of osteochondroma was histopathologically made and she recovered without any sequelae.
Results: As seen in this case, electrophysiological studies play an important role in determining the level of nerve damage, the location of the lesion and the degree of motor and sensorial damage.
Conclusion: Osteochondroma of the fibular head should be considered in differential diagnosis of peroneal neuropathy associated with drop foot. Early diagnosis and treatment may improve outcome and prevent complications.
Keywords: Drop foot; Electromyography; Osteochondroma; Child; Peroneal nerve entrapment
Recep Kamil Kilic
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Salih Akbas
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Akif Muhtar Ozturk
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Ercan Demir
Gazi University School of Medicine
Turkey
Recep Kamil Kilic
Gazi University School of Medicine Turkey
Gazi University School of Medicine Turkey