Neonatal Amplitude Integrated EEG (aEEG): Contribution to Clinical, Etiologic, and Prognosis
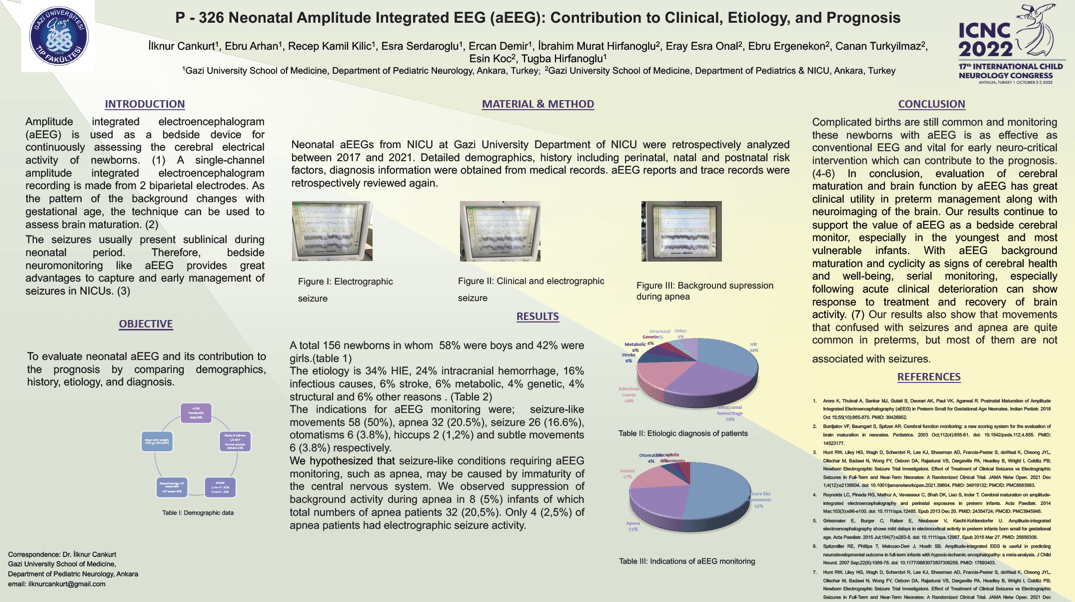
ilknur cankurt, Ebru Arhan, Recep Kamil Kılıç, Esra Serdaroğlu, Ercan Demir, Tuğba HirfanoğluObjective: To evaluate neonatal aEEG and its contribution to the prognosis by comparing demographics, history, etiology, and diagnosis. Material/Methods: Neonates who had an aEEG during their neonatal period at Gazi University Department of NICU between 2017-2021 were retrospectively analyzed. Detailed demographics, history including perinatal period, risk factors, diagnosis, conventional EEG and their relationship between aEEG results were compared. aEEG results were applied to multivariate logistic regression to find the best prognostic factors. Results: A total 156 newborns in whom 58% were boys and 42% were girls. 46% were under 37 weeks. Mode of delivery was spontaneous in 23% and cesarean section in 77% with the birth weight of 2552 g (745-4625g). The etiology is 23% HIE, 20% prematurity, 15% infectious causes, 5% stroke, 5% metabolic and 2% structural. The APGAR score was below 7 in 1 minute in 41% of the patients and in the 5th minute in 23% of the patients. While clinical and electrographical seizures were not observed in 15.3% of the patients, 12% of the patients had myoclonic seizures, 2.5% of the patients had automatism, 17.9% of the patients had clonic seizures, and 28.2% of the patients had apnea and cyanosis. Electrographic seizures were detected in 17.9% of the patients without clinical signs. Overall, aEEG was effective as much as conventional EEG to predict prognosis (p<0.05). Conclusion: Complicated births are still common and monitoring these newborns with aEEG is as effective as conventional EEG and vital for early neuro-critical intervention which can contribute to the prognosis
Keywords: neonatal,aEEG,prognostic
ilknur cankurt
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Ebru Arhan
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Recep Kamil Kılıç
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Esra Serdaroğlu
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Ercan Demir
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Tuğba Hirfanoğlu
Gazi University Faculty ofMedicine
Turkey
Keywords: neonatal,aEEG,prognostic
ilknur cankurt
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Ebru Arhan
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Recep Kamil Kılıç
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Esra Serdaroğlu
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Ercan Demir
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Tuğba Hirfanoğlu
Gazi University Faculty ofMedicine
Turkey
ilknur cankurt
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
Gazi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey