Comparison of 3D Printing Techniques with Patient-Specific Models for Epilepsy Surgery
Ishaan Kumar, Abhi Khapuria, Chip Bobbert, Muhammad Shahzad Zafar, Bilal Berke Ayvaz
Objectives: Recently popular 3D printed patient specific models based on MRI and CT scans may be very helpful for cerebral modeling in epilepsy surgery given the limitations of 2D projection in surgical planning, simulations and patient education. With comparing different techniques directly in scope of epilepsy surgery, we aim to present foresight for providers to adaptate different 3D methods to their own demands.
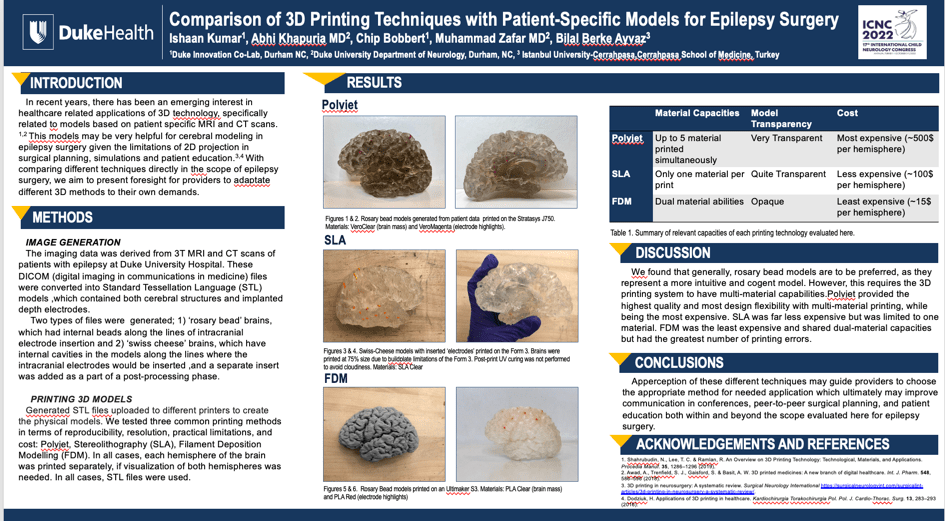
Methods: Imaging data (in DICOM format) derived from 3 Tesla MRI and CT scans from children with epilepsy at Duke University Hospital. By using softwares including 3DSlicer® and MeshMixer®, DICOM data converted into 3D files which contained both cerebral structures and implanted depth electrodes. These files uploaded to different printers to create physical models (Figure-1,2,3). We tested three common printing methods in terms of reproducibility, resolution, practical limitations, and cost: Polyjet, Stereolithography (SLA), Filament Deposition Modelling (FDM).
Results: We found the Polyjet provided the highest quality and most design flexibility with multi-material printing, while being the most expensive. SLA was far less expensive but was limited to one material. FDM was the least expensive and shared dual-material capacities but had the greatest number of printing errors.
Conclusions: Apperception of these different techniques may guide providers to choose the appropriate method for needed application which ultimately may improve communication in conferences, peer-to-peer surgical planning, and patient education both within and beyond the scope evaluated here for epilepsy surgery.
1.Thawani JP et al. 3D printing in neurosurgery: A systematic review. Surgical Neurology International. 2016;7(34):801.
Keywords: 3D printing,epilepsy,patient-specific,neurosurgery,electrode implantation
Ishaan Kumar
Duke University
United States
Abhi Khapuria
Duke University
United States
Chip Bobbert
Duke University
United States
Muhammad Shahzad Zafar
Duke University School of Medicine
United States
Bilal Berke Ayvaz
Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa
Turkey
Objectives: Recently popular 3D printed patient specific models based on MRI and CT scans may be very helpful for cerebral modeling in epilepsy surgery given the limitations of 2D projection in surgical planning, simulations and patient education. With comparing different techniques directly in scope of epilepsy surgery, we aim to present foresight for providers to adaptate different 3D methods to their own demands.
Methods: Imaging data (in DICOM format) derived from 3 Tesla MRI and CT scans from children with epilepsy at Duke University Hospital. By using softwares including 3DSlicer® and MeshMixer®, DICOM data converted into 3D files which contained both cerebral structures and implanted depth electrodes. These files uploaded to different printers to create physical models (Figure-1,2,3). We tested three common printing methods in terms of reproducibility, resolution, practical limitations, and cost: Polyjet, Stereolithography (SLA), Filament Deposition Modelling (FDM).
Results: We found the Polyjet provided the highest quality and most design flexibility with multi-material printing, while being the most expensive. SLA was far less expensive but was limited to one material. FDM was the least expensive and shared dual-material capacities but had the greatest number of printing errors.
Conclusions: Apperception of these different techniques may guide providers to choose the appropriate method for needed application which ultimately may improve communication in conferences, peer-to-peer surgical planning, and patient education both within and beyond the scope evaluated here for epilepsy surgery.
1.Thawani JP et al. 3D printing in neurosurgery: A systematic review. Surgical Neurology International. 2016;7(34):801.
Keywords: 3D printing,epilepsy,patient-specific,neurosurgery,electrode implantation
Ishaan Kumar
Duke University
United States
Abhi Khapuria
Duke University
United States
Chip Bobbert
Duke University
United States
Muhammad Shahzad Zafar
Duke University School of Medicine
United States
Bilal Berke Ayvaz
Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa
Turkey
Bilal Berke Ayvaz
Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa
Turkey
Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa
Turkey