The Treatment By Small Dose Of Sustained Release Valproic Acid For Auditory Hypersensitivity In ASD
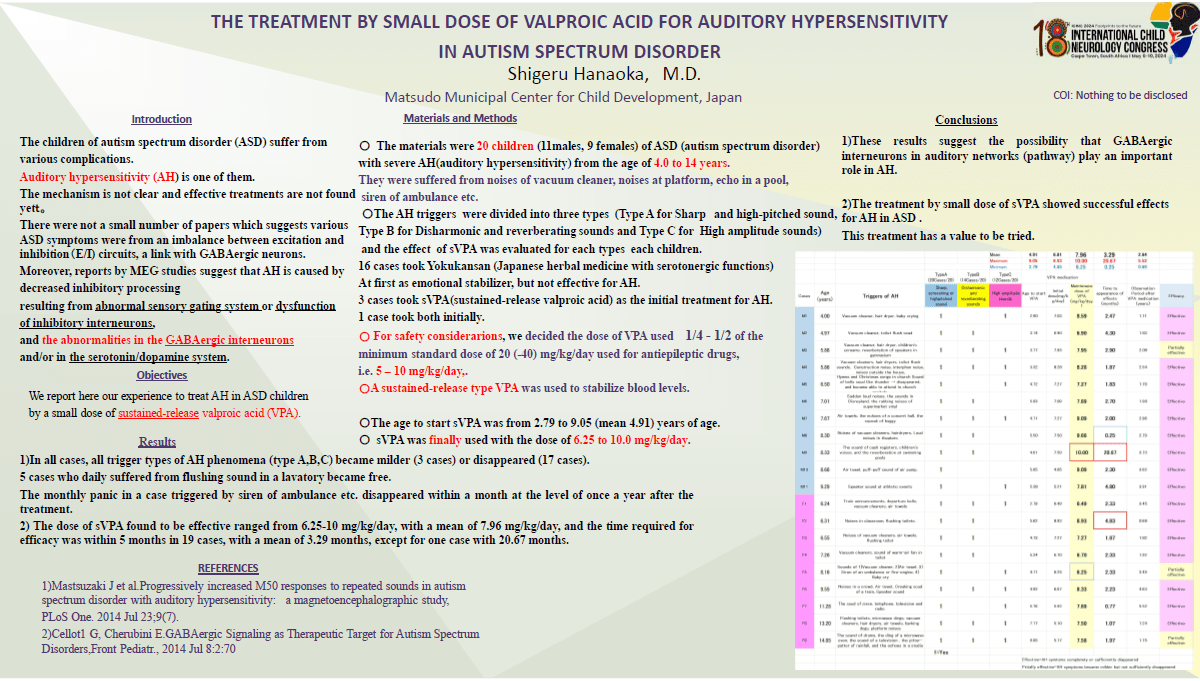
Introduction: The children of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) suffer from various complications. Auditory hypersensitivity (AH) is one of them. The mechanism is not clear and effective treatments are not established. Some reports suggest that AH is caused by decreased inhibitory processing resulting from abnormal sensory gating system or dysfunction of inhibitory interneurons, and the abnormalities in the GABAergic interneurons. We report here our experience to treat AH in ASD children by small dose of sustained release valproic acid (s-VPA). Materials and Methods: The materials were 20 children (11males, 9 females) of ASD with severe AH from the age of 4.0 to 14 years. They were suffered from noises of vacuum cleaner, noises at platform, echo in a pool, siren of ambulance etc. 16 cases took Yokukansan (Japanese herbal medicine with serotonergic functions) at first as emotional stabilizer but not effective for AH. 3 cases took s-VPA as the initial treatment for AH. 1 case took both initially. s-VPA was finally used with the dose of 6.25 to 10.0 mg/kg/day. Results: In all cases, AH phenomena became milder (3 cases) or disappeared (17 cases). 5 cases who daily suffered from flushing sound in a lavatory became free. The monthly panic in a case triggered by siren of ambulance etc. disappeared within a month at the level of once a year after the treatment. Conclusions: The treatment for AH in ASD by small dose of s-VPA showed successful effects. This treatment is simple and has a value to be tried.
HANAOKA Shigeru
Municipal Center for Child Development
Japan