Febrile Seizures In Children With COVID-19 According To COVİD-19 Variant Periods
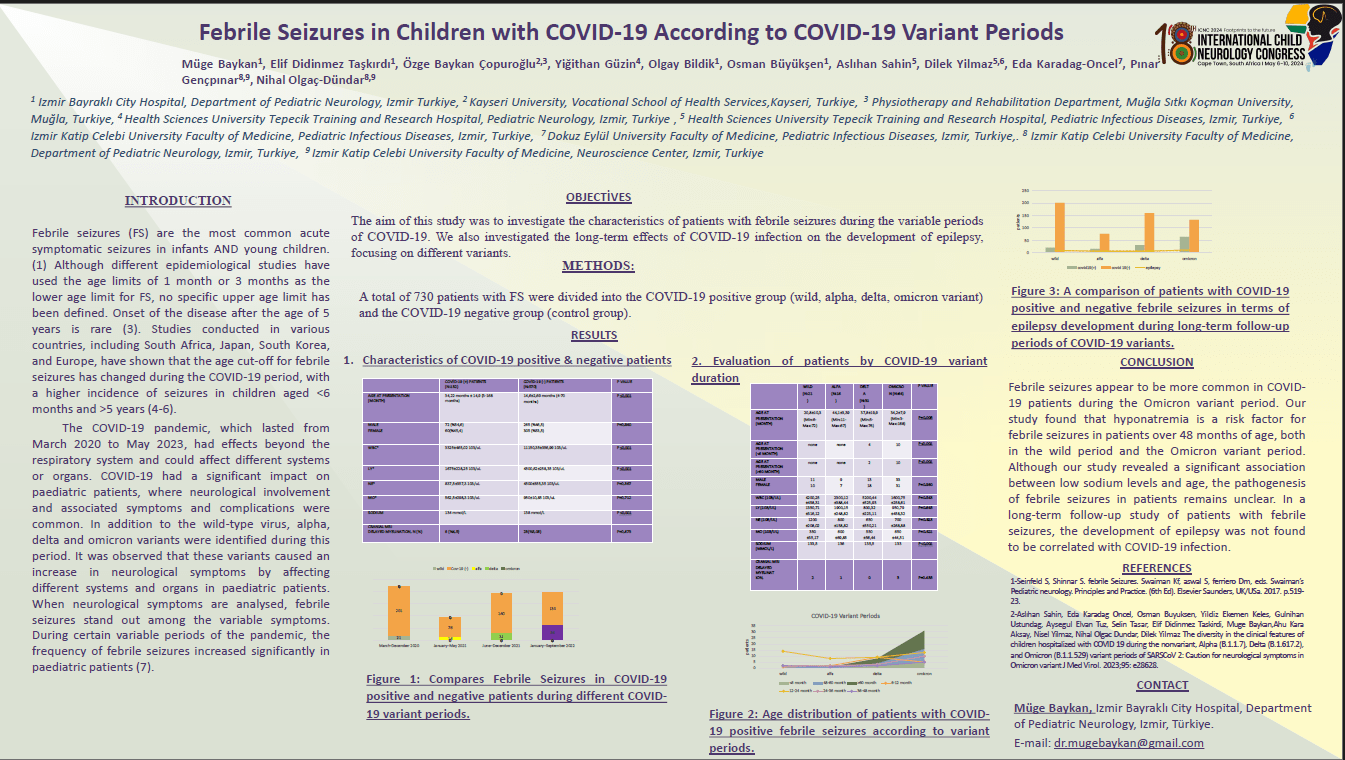
Abstract Objective: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) affected the whole world in 2019. When COVID-19 patients were observed, it was noted that the frequency of febrile seizures (FS) varied in different variant periods. Therefore, this study aimed to elucidate the clinical features of febrile seizures in COVID-19 patients and compare them according to variants.
Methods: In total, 117 patients with FS divided into the COVID-19-positive group (wild, alpha, delta, omicron variant) and the COVID-19-negative group (control group). The clinical characteristics, diagnostic examinations, laboratory test results, treatment outcomes and risk factors were analyzed.
Result: There were 33 patients in the COVID-19 group and 40 patients in the non-COVID-19 group. FS were most commonly observed during the Omicron variant period (p<0.001). Children with COVİD-19 have a later age at onset of FS (p=0.045). There is a significant correlation between neutrophil and monocyte variables (r=0.4832, p<0.001). Hyponatremia in patients with FS with COVİD-19 during the wild and omicron variant period (p<0.001). Calcium values were found to be lower in FS patients with covid-19 during the alpha variant period. (p = 0.034)
Conclusion: Among COVID-19 variants, it was determined that febrile seizures were most frequent in the Omicron variant. The age at onset of febrile seizures was found to be older in COVID-19 patients. Low calcium levels during the COVID-19 alpha variant period and low sodium levels during the wild and omicron variant periods increase the risk of febrile seizures.
müge baykan
Health Sciences University Tepecik Training and Research Hospital
Turkey
elif didinmez taşkırdı
Health Sciences University Tepecik Training and Research Hospital
Turkey
olgay bildik
Health Sciences University Tepecik Training and Research Hospital
Turkey
osman büyükşen
Health Sciences University Tepecik Training and Research Hospital
Turkey
aslıhan şahin
Health Sciences University Tepecik Training and Research Hospital
Turkey
dilek yılmaz
Izmir Katip Celebi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
eda karadağ öncel
Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
pınar gençpınar
Izmir Katip Celebi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey
nihal olgaç dündar
Izmir Katip Celebi University Faculty of Medicine
Turkey