Page 6 - ILAE_Lectures_2015
P. 6
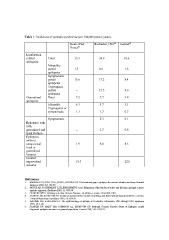
Table 1. Incidences of epileptic syndromes (per 100,000 person years).
South-West Rochester, USA44 Iceland35
France43
Localisation-
related Total 15.3 34.9 18.6
epilepsies
Idiopathic
partial 1.7 0.2 1.6
epilepsies
Symptomatic
partial 13.6 17.2 8.4
epilepsies
Cryptogenic
partial 17.5 8.6
epilepsies
Generalised Total 7.2 7.7 3.9
epilepsies
Idiopathic 6.1 3.7 3.1
Cryptogenic or
symptomatic 1.1 1.7 0.7
Symptomatic 2.3 0.1
1.7 0.8
Epilepsies with 1.9 8.0 8.5
both
generalised and 18.3 22.8
focal features
Epilepsies
without
unequivocal
focal or
generalised
features
Isolated
unprovoked
seizures
References
1. MEINARDI H, SCOTT RA, REIS R, SANDER JW. The treatment gap in epilepsy: the current situation and ways forward.
Epilepsia 2001; 42: 136-49.
2. NGUGI AK, BOTTEMLEY C, KLEINSCHMIDT I et al. Estimation of the burden of active and life-time epilepsy: a meta-
analytic approach. Epilepsia 2010; 51: 883-90.
3. GOWERS WRG. Epilepsy and other chronic diseases. 1st edition. London: Churchill, 1881.
4. SANDER JW, SHORVON SD. Incidence and prevalence studies in epilepsy and their methodological problems: a review.
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1987; 50: 829-39.
5. HAUSER WA, KURLAND LT. The epidemiology of epilepsy in Rochester, Minnesota, 1935 through 1967. Epilepsia
1975; 16: 1-66.
6. SANDER JW, HART YM, JOHNSON AL, SHORVON SD. National General Practice Study of Epilepsy: newly
diagnosed epileptic seizures in a general population. Lancet 1990; 336: 1267-71.