Co-morbid psychiatric disorders in patients with arachnoid cyst: A case series
Yeliz Engindereli, Burçin Şanlıdağ, Mehmet Alp Dirik, Eray Dirik
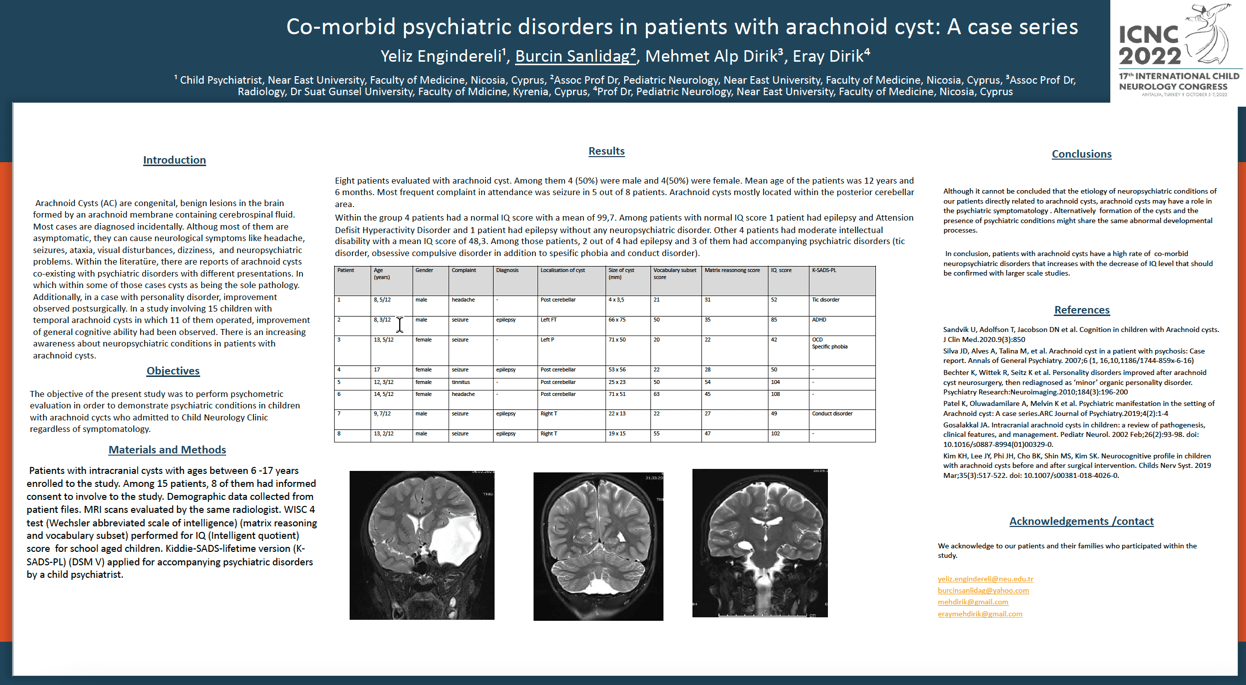
Objective: Arachnoid Cysts (AC) are congenital, benign lesions in the brain formed by an archnoid membrane containing cerebrospinal fluid. Most cases are diagnosed incidentally. Althoug most of them are asymptomatic, they can cause neurological symptoms like headache, seizures and neuropsychiatric problems. Methods: Patients with intracranial cysts with ages between 6 -17 years enrolled to the study. WISC 4 test (Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence) (matrix reasoning and vocabulary subset) performed for IQ (Intelligent quotient) score and shedule for affective disorders ans schizophreniafor school aged children kiddie-SADS-lifetime version (K-SADS-PL) (DSM V) applied for accompanying psychiatric disorders. Results: Eight patients evaluated with arachnoid cyst. Among them 4 (50%) were male and 4(50%) were female. Out of 4 had normal IQ score with a mean of 99,7. Among patients with normal IQ score 1 patient had epilepsy and Attension Defisit Hyperactivity Disorder. Other 4 patients had moderate intellectual disability with a mean IQ score of 48,3. Among those patients 2 out of 4 had epilepsy and 3 of them had accompanying psychiatric disorders (tic disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder in addition to spesific phobia and conduct disorder). Conclusion: In conclusion, patients with arachnoid cysts have a high risk for co-morbid conditions that increases with the decrease of IQ level.
Keywords: arachnoid cyst, pediatric, psychiatric disorders
Yeliz Engindereli
Near East University
Cyprus
Burçin Şanlıdağ
Cyprus
Mehmet Alp Dirik
Dr Suat Günsel University
Cyprus
Eray Dirik
Cyprus
Objective: Arachnoid Cysts (AC) are congenital, benign lesions in the brain formed by an archnoid membrane containing cerebrospinal fluid. Most cases are diagnosed incidentally. Althoug most of them are asymptomatic, they can cause neurological symptoms like headache, seizures and neuropsychiatric problems. Methods: Patients with intracranial cysts with ages between 6 -17 years enrolled to the study. WISC 4 test (Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence) (matrix reasoning and vocabulary subset) performed for IQ (Intelligent quotient) score and shedule for affective disorders ans schizophreniafor school aged children kiddie-SADS-lifetime version (K-SADS-PL) (DSM V) applied for accompanying psychiatric disorders. Results: Eight patients evaluated with arachnoid cyst. Among them 4 (50%) were male and 4(50%) were female. Out of 4 had normal IQ score with a mean of 99,7. Among patients with normal IQ score 1 patient had epilepsy and Attension Defisit Hyperactivity Disorder. Other 4 patients had moderate intellectual disability with a mean IQ score of 48,3. Among those patients 2 out of 4 had epilepsy and 3 of them had accompanying psychiatric disorders (tic disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder in addition to spesific phobia and conduct disorder). Conclusion: In conclusion, patients with arachnoid cysts have a high risk for co-morbid conditions that increases with the decrease of IQ level.
Keywords: arachnoid cyst, pediatric, psychiatric disorders
Yeliz Engindereli
Near East University
Cyprus
Burçin Şanlıdağ
Cyprus
Mehmet Alp Dirik
Dr Suat Günsel University
Cyprus
Eray Dirik
Cyprus
Yeliz Engindereli
Near East University
Cyprus