Assessment of Nutritional Status, Resuscitation Modalities of Malnutrition, and Enteral Feeding Products for Children with Neurological Disorders
Burce Emine Dortkardesler, Seda Kanmaz, Ozlem Yilmaz, Gursel Sen, Yavuz Atas, Cemile Busra Olculu, Tugce Ince, Dilara Ece Toprak, Hepsen Mine Serin, Sanem Keskin Yilmaz, Gul Aktan, Sarenur Gokben, Hediye Reyhan, Dogan Barut, Miray Karakoyun, Funda Cetin, Nuri Zafer Kurugol, Sema Aydogdu, Hasan Tekgul
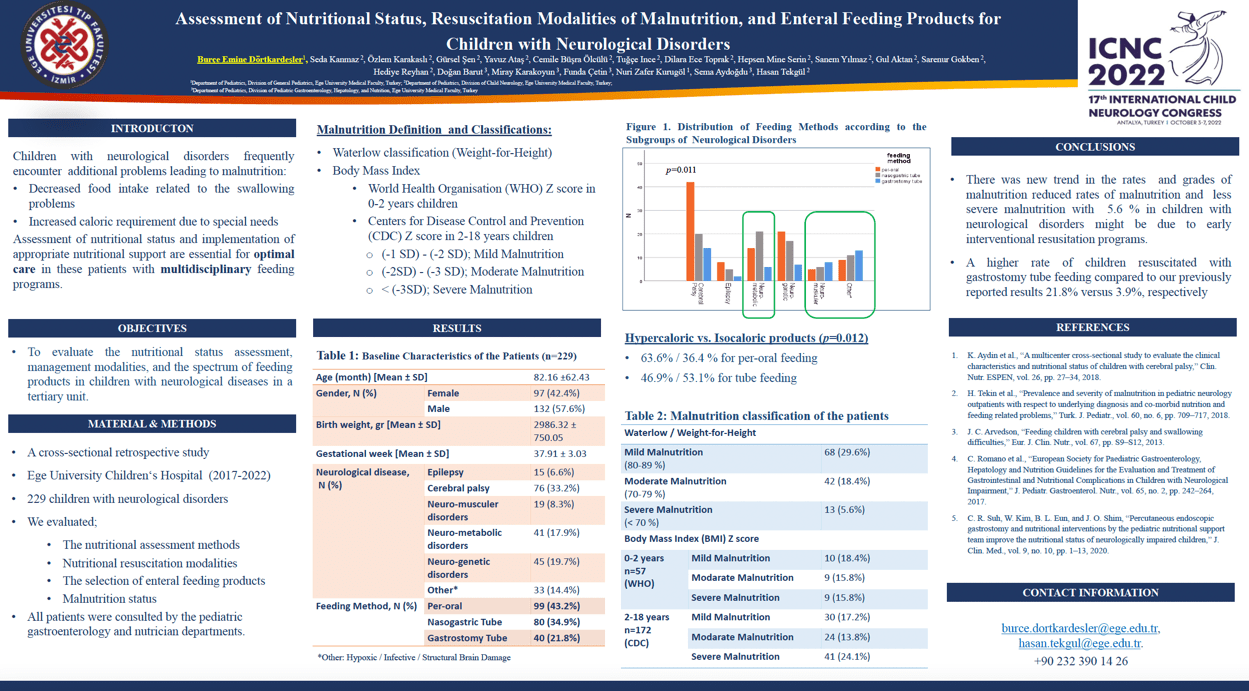
Objective: Children with neurological disorders are frequently associated with factors leading to malnutrition, such as decreased food intake, increased nutrient loss, and nutrient requirement. Assessment of nutritional status and implementation of appropriate nutritional support are essential for the optimal care of these patients in multidisciplinary feeding programs. To evaluate nutritional status assessment, management modalities, and the spectrum of feeding products in children with neurological diseases in the tertiary unit. Methods. A cross-sectional retrospective study cohort consisted of 226 children with neurological disorders who were evaluated for nutritional assessment in the University Pediatric Neurology Clinic between 2017 and 2022. We evaluated the nutritional assessment methods, nutritional resuscitation modalities, and the selection spectrum of enteral feeding products in the cohort. All patients were consulted by the pediatric gastroenterology department. Results. Nutritional resuscitation was managed with gastrostomy tube feeding in 50 children (21.8%), nasogastric tube feeding in 80 (34.9%), and the remaining with per-oral feeding (43.2%). The spectrum of enteral feeding products in the cohort was: hypercaloric versus isocaloric products = 63.6%/36.4% for oral feeding, 46.9%/53.1% for tube feeding, p = 0.012). Conclusion. When compared to our previously reported results (3.9%), there was a significantly higher number of children resuscitated with gastrostomy tube feeding. This situation is attributed to the fact that our hospital is a tertiary level unit and the adaptability of our healthcare professionals to the nutritional assessment and management modalities of nutrition-related problems in children with neurological disorders.
Keywords: Malnutrition, Enteral Feeding, Neurological Disorders, Nutritional Resuscitation Modalities
Burce Emine Dortkardesler
Ege University
Turkey
Seda Kanmaz
Ege University
Turkey
Ozlem Yilmaz
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Gursel Sen
Ege University
Turkey
Yavuz Atas
Ege University
Turkey
Cemile Busra Olculu
Ege University
Turkey
Tugce Ince
Ege University
Turkey
Dilara Ece Toprak
Ege University
Turkey
Objective: Children with neurological disorders are frequently associated with factors leading to malnutrition, such as decreased food intake, increased nutrient loss, and nutrient requirement. Assessment of nutritional status and implementation of appropriate nutritional support are essential for the optimal care of these patients in multidisciplinary feeding programs. To evaluate nutritional status assessment, management modalities, and the spectrum of feeding products in children with neurological diseases in the tertiary unit. Methods. A cross-sectional retrospective study cohort consisted of 226 children with neurological disorders who were evaluated for nutritional assessment in the University Pediatric Neurology Clinic between 2017 and 2022. We evaluated the nutritional assessment methods, nutritional resuscitation modalities, and the selection spectrum of enteral feeding products in the cohort. All patients were consulted by the pediatric gastroenterology department. Results. Nutritional resuscitation was managed with gastrostomy tube feeding in 50 children (21.8%), nasogastric tube feeding in 80 (34.9%), and the remaining with per-oral feeding (43.2%). The spectrum of enteral feeding products in the cohort was: hypercaloric versus isocaloric products = 63.6%/36.4% for oral feeding, 46.9%/53.1% for tube feeding, p = 0.012). Conclusion. When compared to our previously reported results (3.9%), there was a significantly higher number of children resuscitated with gastrostomy tube feeding. This situation is attributed to the fact that our hospital is a tertiary level unit and the adaptability of our healthcare professionals to the nutritional assessment and management modalities of nutrition-related problems in children with neurological disorders.
Keywords: Malnutrition, Enteral Feeding, Neurological Disorders, Nutritional Resuscitation Modalities
Burce Emine Dortkardesler
Ege University
Turkey
Seda Kanmaz
Ege University
Turkey
Ozlem Yilmaz
Ege University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Gursel Sen
Ege University
Turkey
Yavuz Atas
Ege University
Turkey
Cemile Busra Olculu
Ege University
Turkey
Tugce Ince
Ege University
Turkey
Dilara Ece Toprak
Ege University
Turkey
Burce Emine Dortkardesler
Ege University Turkey
Ege University Turkey