Epileptic encephalopathy, visual impairment and developmental retardation: CDKL5 deficiency disorder
Betül Kılıç, Esra Özpınar, Yasemin Topçu, Mehmet Palaz, Kürşad Aydın
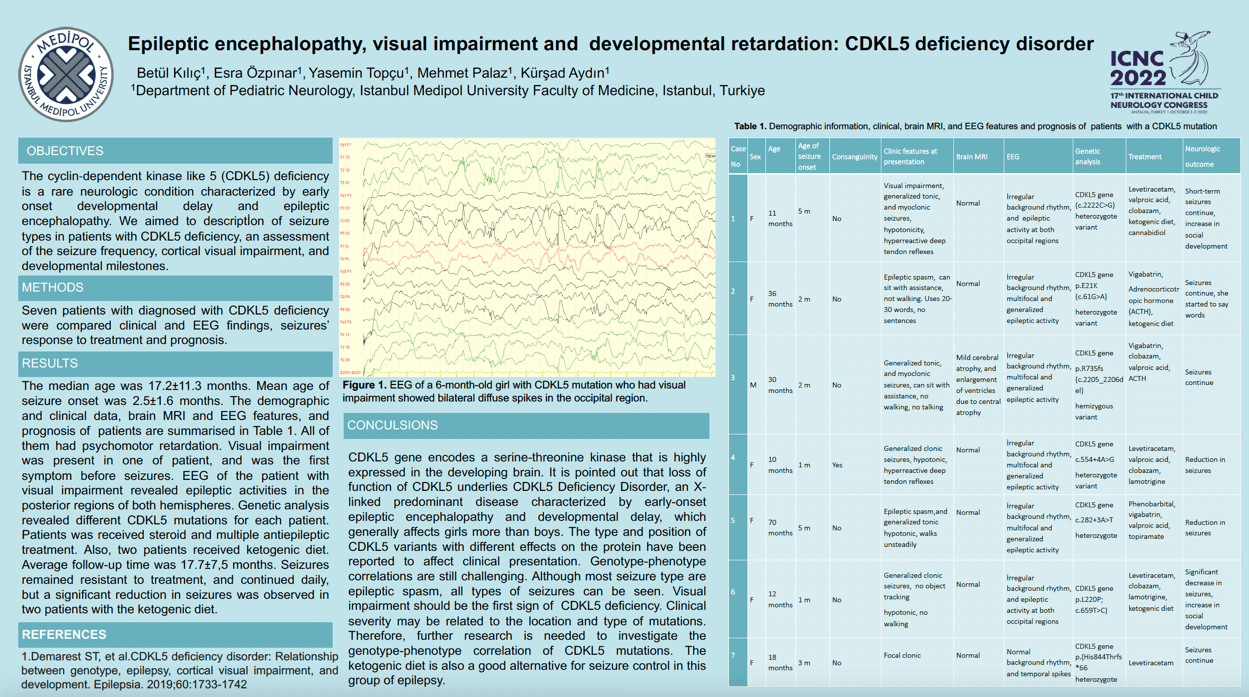
Objectives: The cyclin‐dependent kinase like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency is a rare neurologic condition characterized by early onset developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. We aimed to descript of seizure types in patients with CDKL5 deficiency, an assessment of the seizure frequency, cortical visual impairment, and developmental milestones. Methods: Seven patients with diagnosed with CDKL5 deficiency were compared clinical and EEG findings, seizures’ response to treatment and prognosis. Results: The median age was 17.2±11.3 months. Mean age of seizure onset was 2.5±1.6 months. The demographic and clinical data, brain MRI and EEG features, and prognosis of patients are summarised in Table 1. All of them had psychomotor retardation. Visual impairment was present in one of patient, and was the first symptom before seizures. EEG of the patient with visual impairment revealed epileptic activities in the posterior regions of both hemispheres. Mutational analysis revealed different CDKL5 mutations for each patient. Patients was received multiple antiepileptic, and steroid treatment. Also, two patients received ketogenic diet. Average follow-up time was 17.7±7,5 months. Seizures remained resistant to treatment, and daily continued, but a significant reduction in seizures was observed in two patients with the ketogenic diet. Conclusions: Early onset epilepsy with severe psychomotor retardation without a known etiology may be caused by a mutation in CDKL5. Although most seizure type are epileptic spasm, all types of seizures can be seen. Visual impairment should be the first sign of CDKL5 deficiency. The ketogenic diet is also a good alternative for seizure control in this group of epilepsy.
Keywords: CDKL5, epileptic encephalopathy, visual impairment
Betül Kılıç
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Esra Özpınar
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Yasemin Topçu
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Mehmet Palaz
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Kürşad Aydın
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Objectives: The cyclin‐dependent kinase like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency is a rare neurologic condition characterized by early onset developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. We aimed to descript of seizure types in patients with CDKL5 deficiency, an assessment of the seizure frequency, cortical visual impairment, and developmental milestones. Methods: Seven patients with diagnosed with CDKL5 deficiency were compared clinical and EEG findings, seizures’ response to treatment and prognosis. Results: The median age was 17.2±11.3 months. Mean age of seizure onset was 2.5±1.6 months. The demographic and clinical data, brain MRI and EEG features, and prognosis of patients are summarised in Table 1. All of them had psychomotor retardation. Visual impairment was present in one of patient, and was the first symptom before seizures. EEG of the patient with visual impairment revealed epileptic activities in the posterior regions of both hemispheres. Mutational analysis revealed different CDKL5 mutations for each patient. Patients was received multiple antiepileptic, and steroid treatment. Also, two patients received ketogenic diet. Average follow-up time was 17.7±7,5 months. Seizures remained resistant to treatment, and daily continued, but a significant reduction in seizures was observed in two patients with the ketogenic diet. Conclusions: Early onset epilepsy with severe psychomotor retardation without a known etiology may be caused by a mutation in CDKL5. Although most seizure type are epileptic spasm, all types of seizures can be seen. Visual impairment should be the first sign of CDKL5 deficiency. The ketogenic diet is also a good alternative for seizure control in this group of epilepsy.
Keywords: CDKL5, epileptic encephalopathy, visual impairment
Betül Kılıç
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Esra Özpınar
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Yasemin Topçu
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Mehmet Palaz
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Kürşad Aydın
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Esra Özpınar
Medipol University Medical Faculty Turkey
Medipol University Medical Faculty Turkey