Ketogenic diet treatment success in our two patients with epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures
Betül Kılıç, Esra Özpınar, Mehmet Palaz, Yasemin Topçu, Kürşad Aydın
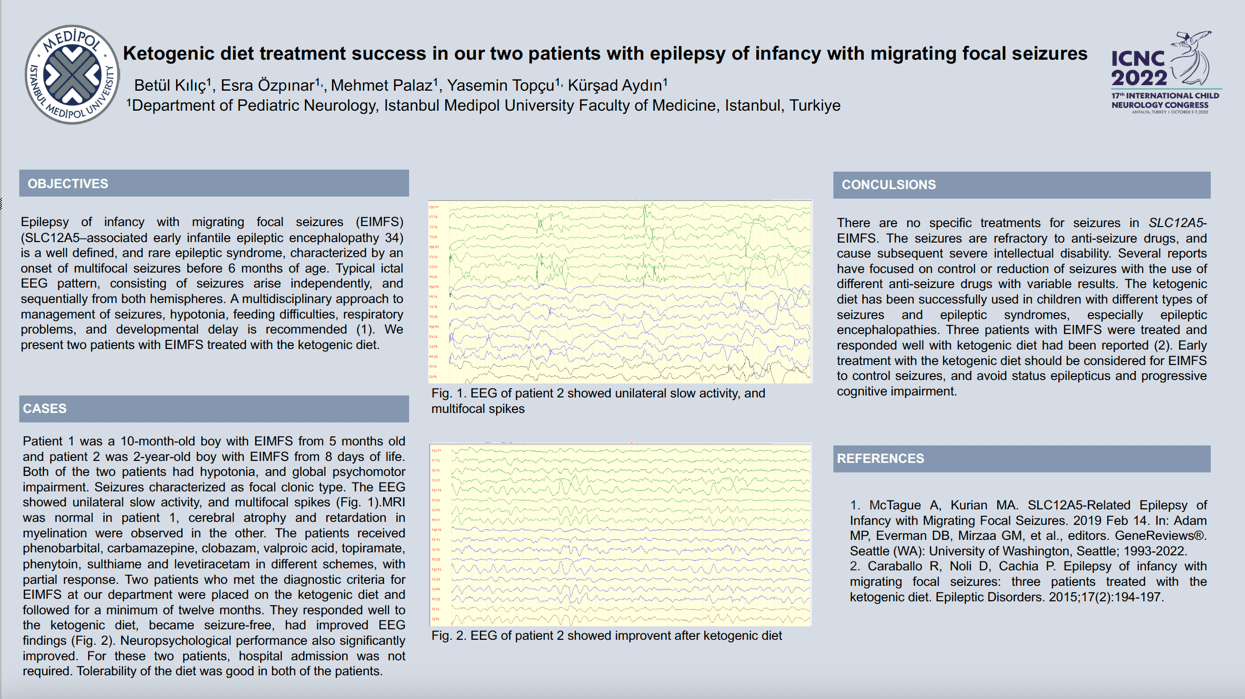
Objectives: Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures (EIMFS) (SLC12A5 –associated early infantile epileptic encephalopathy 34) is a well defined and rare epileptic syndrome, characterized by an onset of multifocal seizures before 6 months of age and a typical ictal EEG pattern, consisting of seizures that arise independently and sequentially from both hemispheres. The seizures are refractory to antiepileptic drugs and cause subsequent severe intellectual disability. Several reports have focused on control or reduction of seizures with the use of different antiepileptic drugs with variable results . The ketogenic diet has been successfully used in children, especially epileptic encephalopathies. We present two patients with epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures treated with the ketogenic diet. Methods:Two patients who met the diagnostic criteria for EIMFS at our department were placed on the ketogenic diet and followed for a minimum of twelve months. Results:Both of the two patients had hypotonia, and global psychomotor impairment. Seizures characterized focal clonic focal clonic type. The EEG showed unilateral slow activity, amd multifocal spikes. MRI was normal in one patient, and cerebral atrophy and retardation in myelination were observed in the other. They responded well to the ketogenic diet, became seizure-free and neuropsychological performance also significantly improved. For these two patients hospital admission was not required. Tolerability of the diet was good in both of the patients. Conclusion:Early treatment with the ketogenic diet should be considered for epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures to control seizures and avoid status epilepticus and progressive cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Migrating focal seizures, SLC12A5, ketogenic diet treatment
Betül Kılıç
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Esra Özpınar
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Mehmet Palaz
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Yasemin Topçu
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Kürşad Aydın
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Objectives: Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures (EIMFS) (SLC12A5 –associated early infantile epileptic encephalopathy 34) is a well defined and rare epileptic syndrome, characterized by an onset of multifocal seizures before 6 months of age and a typical ictal EEG pattern, consisting of seizures that arise independently and sequentially from both hemispheres. The seizures are refractory to antiepileptic drugs and cause subsequent severe intellectual disability. Several reports have focused on control or reduction of seizures with the use of different antiepileptic drugs with variable results . The ketogenic diet has been successfully used in children, especially epileptic encephalopathies. We present two patients with epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures treated with the ketogenic diet. Methods:Two patients who met the diagnostic criteria for EIMFS at our department were placed on the ketogenic diet and followed for a minimum of twelve months. Results:Both of the two patients had hypotonia, and global psychomotor impairment. Seizures characterized focal clonic focal clonic type. The EEG showed unilateral slow activity, amd multifocal spikes. MRI was normal in one patient, and cerebral atrophy and retardation in myelination were observed in the other. They responded well to the ketogenic diet, became seizure-free and neuropsychological performance also significantly improved. For these two patients hospital admission was not required. Tolerability of the diet was good in both of the patients. Conclusion:Early treatment with the ketogenic diet should be considered for epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures to control seizures and avoid status epilepticus and progressive cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Migrating focal seizures, SLC12A5, ketogenic diet treatment
Betül Kılıç
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Esra Özpınar
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Mehmet Palaz
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Yasemin Topçu
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Kürşad Aydın
Medipol University Medical Faculty
Turkey
Esra Özpınar
Medipol University Medical Faculty Turkey
Medipol University Medical Faculty Turkey