Macrocephaly/autism syndrome exhibits neuroradiological abnormalities including Arnold-Chiari syndrome type I: Clinico-radiological spectrum of a PTEN-opathy
Tuğçe Aksu Uzunhan, Bülent Kara, Adnan Deniz , Biray Ertürk, Kürşad Aydın, Pınar Öz, Mehpare Özkan, Betül Kılıç, Deniz Sünnetçi Akkoyunlu
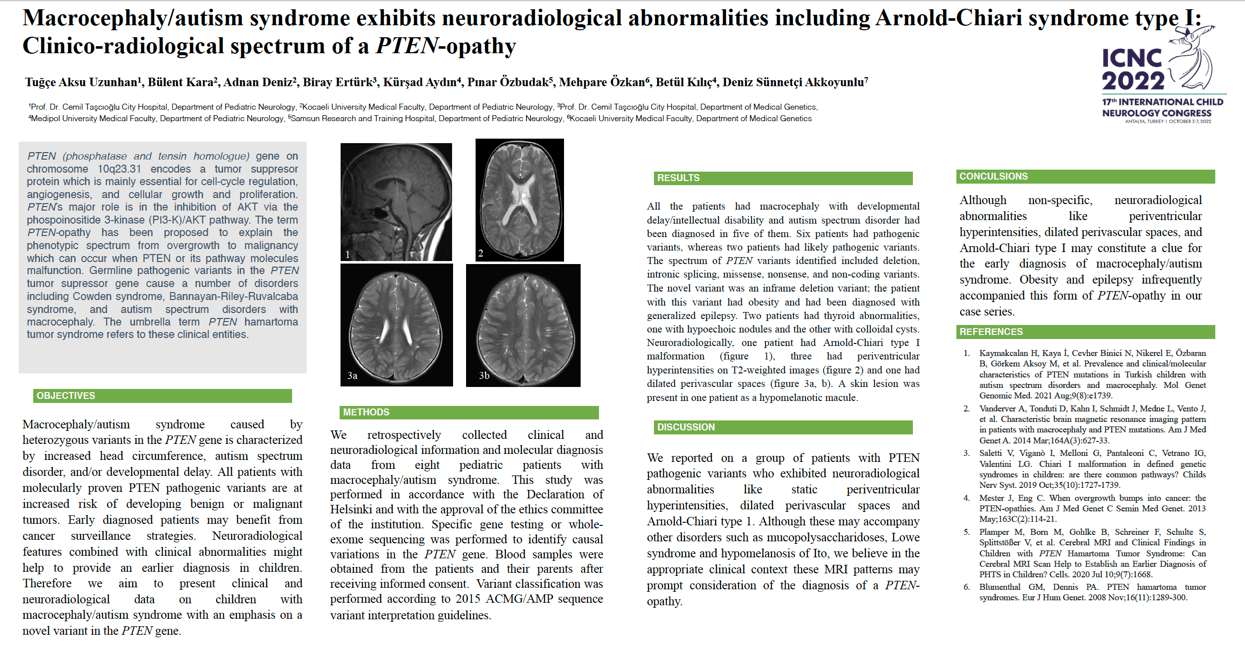
Objectives Macrocephaly/autism syndrome, which is characterized by increased head circumference, autism spectrum disorder, and/or developmental delay, and PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome are both caused by heterozygous variants in the PTEN gene. We aim to present clinical and neuroradiological data on children with macrocephaly/autism syndrome with an emphasis on a novel variant in the PTEN gene. Methods We retrospectively collected clinical and neuroradiological information and molecular diagnosis data from eight pediatric patients with macrocephaly/autism syndrome. Specific gene testing or whole-exome sequencing was performed to identify causal variations in the PTEN gene. Results All the patients had macrocephaly with developmental delay/intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder had been diagnosed in five of them. Six patients had pathogenic variants, whereas two patients had likely pathogenic variants. The spectrum of PTEN variants identified included deletion, intronic splicing, missense, nonsense, and non-coding variants. The novel variant was an inframe deletion variant; the patient with this variant had obesity and had been diagnosed with generalized epilepsy. Two patients had thyroid abnormalities, one with hypoechoic nodules and the other with colloidal cysts. Neuroradiologically, one patient had Arnold-Chiari type I malformation, three had periventricular hyperintensities on T2-weighted images and one had dilated perivascular spaces. A skin lesion was present in one patient as a hypomelanotic macule. Conclusion Although non-specific, neuroradiological abnormalities like periventricular hyperintensities, dilated perivascular spaces, and Arnold-Chiari type I may constitute a clue for the early diagnosis of macrocephaly/autism syndrome. Obesity and epilepsy infrequently accompanied this form of PTEN-opathy in our case series.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders, developmental delay, perivascular spaces, periventricular hyperintensities, PTEN
Tuğçe Aksu Uzunhan
Turkey
Bülent Kara
Adnan Deniz
Biray Ertürk
Kürşad Aydın
Pınar Öz
Mehpare Özkan
Betül Kılıç
Deniz Sünnetçi Akkoyunlu
Objectives Macrocephaly/autism syndrome, which is characterized by increased head circumference, autism spectrum disorder, and/or developmental delay, and PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome are both caused by heterozygous variants in the PTEN gene. We aim to present clinical and neuroradiological data on children with macrocephaly/autism syndrome with an emphasis on a novel variant in the PTEN gene. Methods We retrospectively collected clinical and neuroradiological information and molecular diagnosis data from eight pediatric patients with macrocephaly/autism syndrome. Specific gene testing or whole-exome sequencing was performed to identify causal variations in the PTEN gene. Results All the patients had macrocephaly with developmental delay/intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder had been diagnosed in five of them. Six patients had pathogenic variants, whereas two patients had likely pathogenic variants. The spectrum of PTEN variants identified included deletion, intronic splicing, missense, nonsense, and non-coding variants. The novel variant was an inframe deletion variant; the patient with this variant had obesity and had been diagnosed with generalized epilepsy. Two patients had thyroid abnormalities, one with hypoechoic nodules and the other with colloidal cysts. Neuroradiologically, one patient had Arnold-Chiari type I malformation, three had periventricular hyperintensities on T2-weighted images and one had dilated perivascular spaces. A skin lesion was present in one patient as a hypomelanotic macule. Conclusion Although non-specific, neuroradiological abnormalities like periventricular hyperintensities, dilated perivascular spaces, and Arnold-Chiari type I may constitute a clue for the early diagnosis of macrocephaly/autism syndrome. Obesity and epilepsy infrequently accompanied this form of PTEN-opathy in our case series.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders, developmental delay, perivascular spaces, periventricular hyperintensities, PTEN
Tuğçe Aksu Uzunhan
Turkey
Bülent Kara
Adnan Deniz
Biray Ertürk
Kürşad Aydın
Pınar Öz
Mehpare Özkan
Betül Kılıç
Deniz Sünnetçi Akkoyunlu
Tuğçe Aksu Uzunhan
Turkey
Turkey