Successful management of Pediatric-onset Multiple sclerosis with Ocrelizumab
Nisreen Bader , Khurshid Khan, Amal Sherif, Aman Sohal
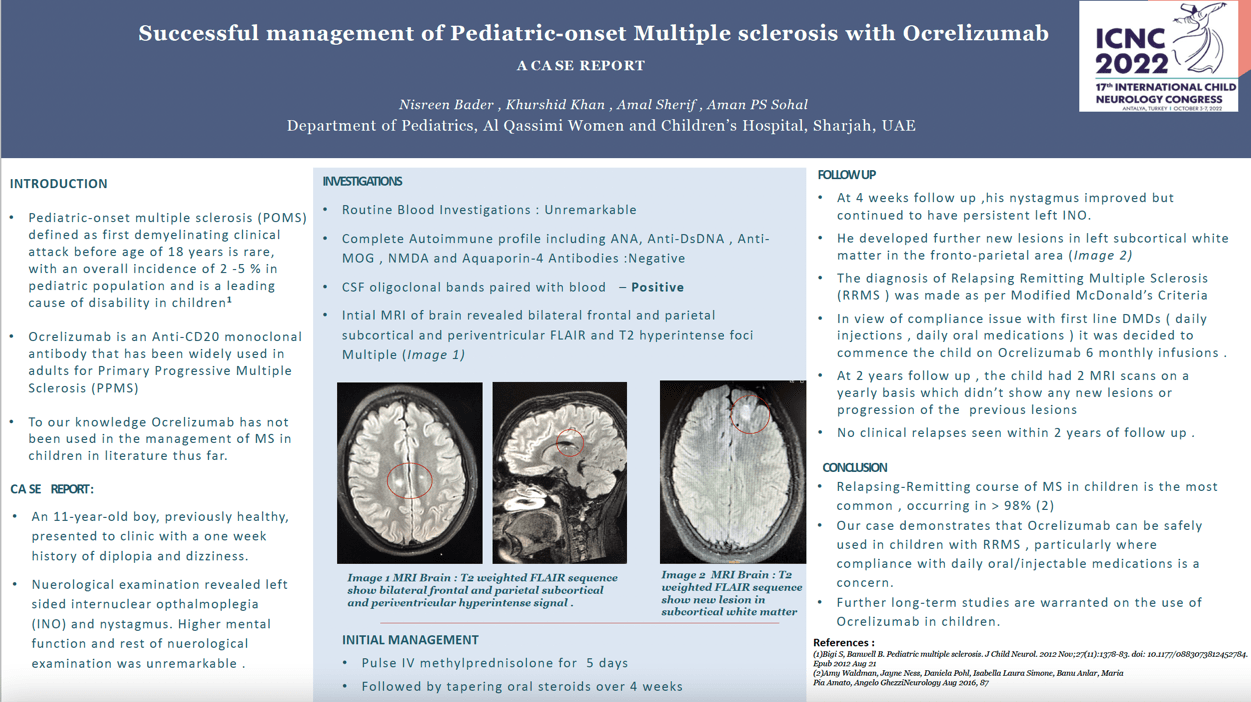
Introduction: Pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis is rare with an overall incidence of 2 -5 % among pediatric population and one of the leading causes of neurodisability in children. Although numerous disease-modifying drugs (DMD’S) have been used in the management of POMS, to our knowledge Ocrelizumab has not been reported in the management of Multiple Sclerosis in children. Methods and Results: A previously healthy 11-years-old boy presented with new onset diplopia with headache. He underwent MRI brain scan which revealed multiple hyperintense foci in subcortical and periventricular white matter on T2-weighted imaging without restricted diffusion. MRI spine was normal. Extensive workup including routine labs, autoimmune profile (ANA, Ds-DNA, ANCA, Anti-cardiolipin and Aquaporin-4 antibodies, NMDA and anti-MOG antibodies) were negative. CSF analysis showed positive oligoclonal bands. The child was initially treated with pulsed intravenous steroids followed by tapering course of oral steroids with reasonable improvement. A follow up MRI brain revealed increase in the white matter signal abnormalities suggesting dissemination in space and time confirming diagnosis of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Various DMD’s were discussed with family but due to risk of non-compliance to daily oral and injectable drugs Ocrelizumab was commenced as 6-monthly infusions. Patient showed a significant clinical response with no clinical relapses and stable MRI scans with no new lesions at 18-month follow up Conclusion: Our case report suggests Ocrelizumab use as an alternative DMD in pediatric-onset Multiple sclerosis who are at risk of non-compliance to standard MS medications. To our knowledge ours is a first case of use of Ocrelizumab.
Keywords: Pediatric onset multiple sclerosis, Ocrelizumab
Nisreen Bader
EHS
United Arab Emirates
Khurshid Khan
EHS
United Arab Emirates
Amal Sherif
EHS
United Arab Emirates
Aman Sohal
United Arab Emirates
Introduction: Pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis is rare with an overall incidence of 2 -5 % among pediatric population and one of the leading causes of neurodisability in children. Although numerous disease-modifying drugs (DMD’S) have been used in the management of POMS, to our knowledge Ocrelizumab has not been reported in the management of Multiple Sclerosis in children. Methods and Results: A previously healthy 11-years-old boy presented with new onset diplopia with headache. He underwent MRI brain scan which revealed multiple hyperintense foci in subcortical and periventricular white matter on T2-weighted imaging without restricted diffusion. MRI spine was normal. Extensive workup including routine labs, autoimmune profile (ANA, Ds-DNA, ANCA, Anti-cardiolipin and Aquaporin-4 antibodies, NMDA and anti-MOG antibodies) were negative. CSF analysis showed positive oligoclonal bands. The child was initially treated with pulsed intravenous steroids followed by tapering course of oral steroids with reasonable improvement. A follow up MRI brain revealed increase in the white matter signal abnormalities suggesting dissemination in space and time confirming diagnosis of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Various DMD’s were discussed with family but due to risk of non-compliance to daily oral and injectable drugs Ocrelizumab was commenced as 6-monthly infusions. Patient showed a significant clinical response with no clinical relapses and stable MRI scans with no new lesions at 18-month follow up Conclusion: Our case report suggests Ocrelizumab use as an alternative DMD in pediatric-onset Multiple sclerosis who are at risk of non-compliance to standard MS medications. To our knowledge ours is a first case of use of Ocrelizumab.
Keywords: Pediatric onset multiple sclerosis, Ocrelizumab
Nisreen Bader
EHS
United Arab Emirates
Khurshid Khan
EHS
United Arab Emirates
Amal Sherif
EHS
United Arab Emirates
Aman Sohal
United Arab Emirates
Nisreen Bader
EHS United Arab Emirates
EHS United Arab Emirates