Is There a Relation Between Hippocampal Measurements and Childhood Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy?
Hilal Altas, Özge Dedeoğlu, Manolya Panpallı, Başak Gülleroğlu, Seçil Ekşioğlu, Neşe Çıtak Kurt
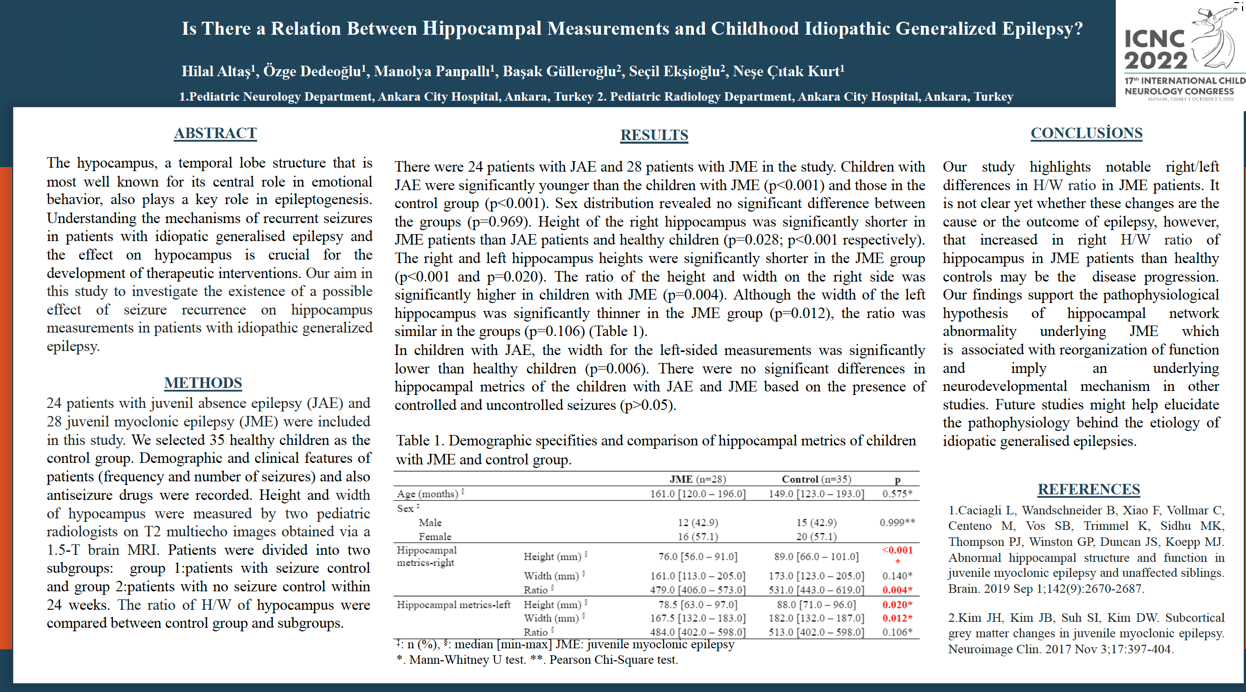
Objective: The hypocampus that is most well known for its central role in emotional behavior, also plays a key role in epileptogenesis. Understanding the mechanisms of recurrent seizures in patients with idiopatic generalised epilepsy and the effect on hypocampus in is crucial for the development of therapeutic interventions that will reduce its severity. Aim: To investigate the existence of a possible effect of seizure recurrence on the measurements of hypocampus in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Methods: We selected 52 patients with childhood absence epilepsy (n=25) and juvenil myoclonic epilepsy (n=27) between 6-16 years. Demographic and clinical features of patients (frequency and number of seizures, antiepileptics) were recorded. Height and width of hypocampus were measured by two pediatric radiologists. Patients were also divided into two subgroups: patients with seizure control and patients with no seizure control within 24 weeks. The ratio of H/W of hypocampus were compared between control group (35 patients) and subgroups. Results: The right H/W ratio of hypocampus was significantly reduced in the JME patients than the healthy controls (p=0.001). There were no significant differences in the H/W ratio of hypocampus of the epileptic children with and without seizure control. Conclusion: Our study highlights notable right/left differences in H/W ratio in JME patients. It is not clear yet whether these changes are the cause or the outcome of epilepsy, however, that decreased in right H/W ratio of hypocampus in JME patients than the healthy controls may be the effect of recurrent seizures.
Keywords: hypocampus, recurrent seizure, epilepsy
Hilal Altas
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Özge Dedeoğlu
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Manolya Panpallı
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Başak Gülleroğlu
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Seçil Ekşioğlu
Ankara City Hospital
Neşe Çıtak Kurt
Ankara City Hospital
Objective: The hypocampus that is most well known for its central role in emotional behavior, also plays a key role in epileptogenesis. Understanding the mechanisms of recurrent seizures in patients with idiopatic generalised epilepsy and the effect on hypocampus in is crucial for the development of therapeutic interventions that will reduce its severity. Aim: To investigate the existence of a possible effect of seizure recurrence on the measurements of hypocampus in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Methods: We selected 52 patients with childhood absence epilepsy (n=25) and juvenil myoclonic epilepsy (n=27) between 6-16 years. Demographic and clinical features of patients (frequency and number of seizures, antiepileptics) were recorded. Height and width of hypocampus were measured by two pediatric radiologists. Patients were also divided into two subgroups: patients with seizure control and patients with no seizure control within 24 weeks. The ratio of H/W of hypocampus were compared between control group (35 patients) and subgroups. Results: The right H/W ratio of hypocampus was significantly reduced in the JME patients than the healthy controls (p=0.001). There were no significant differences in the H/W ratio of hypocampus of the epileptic children with and without seizure control. Conclusion: Our study highlights notable right/left differences in H/W ratio in JME patients. It is not clear yet whether these changes are the cause or the outcome of epilepsy, however, that decreased in right H/W ratio of hypocampus in JME patients than the healthy controls may be the effect of recurrent seizures.
Keywords: hypocampus, recurrent seizure, epilepsy
Hilal Altas
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Özge Dedeoğlu
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Manolya Panpallı
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Başak Gülleroğlu
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Seçil Ekşioğlu
Ankara City Hospital
Neşe Çıtak Kurt
Ankara City Hospital
Hilal Altas
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey
Ankara City Hospital
Turkey