Pediatric Onset Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: A Multicenter Study from Türkiye
Gamze Sarıkaya Uzan, Deniz Yüksel, Erhan Aksoy, Ülkühan Öztoprak, Mehmet Canpolat, Selcan Öztürk, Çelebi Yıldırım, Ayten Güleç, Hüseyin Per, Hakan Gümüş, Çetin Okuyaz, Meltem Çobanoğulları Direk, Mustafa Kömür, Aycan Ünalp, Ünsal Yılmaz, Ömer Bektaş, Serap Teber, Nargiz Aliyeva, Nihal Olgaç Dündar, Pınar Gençpınar, Esra Gürkaş, Sanem Keskin Yılmaz, Seda Kanmaz, Hasan Tekgül, Ayşe Aksoy, Gökçen Öz Tuncer, Elif Acar Arslan, Ayşe Tosun, Müge Ayanoğlu, Muhittin Bodur, Bülent Ünay, Semra Hız Kurul, Uluç Yiş
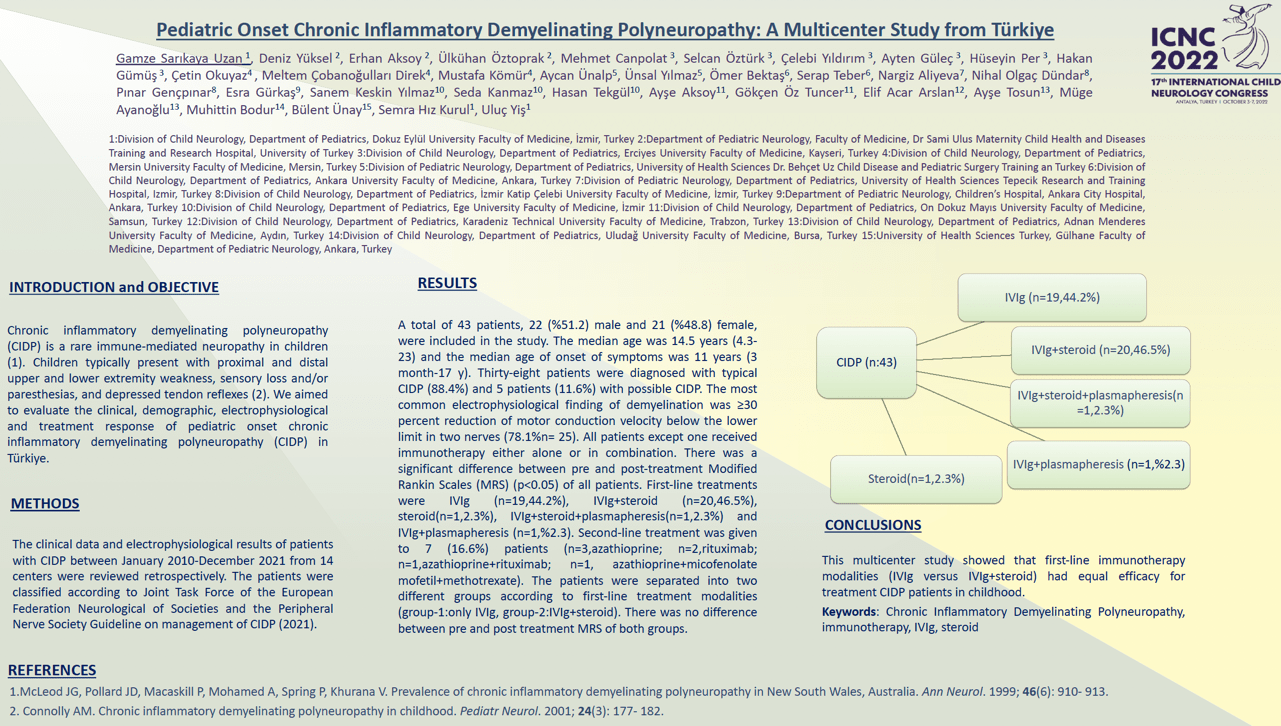
Objective:We aimed to evaluate the clinical, demographic, electrophysiological and treatment response of pediatric onset chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in Türkiye. Methods:The clinical data and electrophysiological results of patients with CIDP between January 2010-December 2021 from 14 centers were reviewed retrospectively. The patients were classified according to Joint Task Force of the European Federation Neurological of Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of CIDP (2021). Results:A total of 43 patients, 22 (%51.2) male and 21 (%48.8) female, were included in the study. The median age was 14.5 years (4.3-23) and the median age of onset of symptoms was 11 years (3 month-17 y). Thirty-eight patients were diagnosed with typical CIDP (88.4%) and 5 patients (11.6%) with possible CIDP. The most common electrophysiological finding of demyelination was ≥30 percent reduction of motor conduction velocity below the lower limit in two nerves (78.1%n= 25). All patients except one received immunotherapy either alone or in combination. There was a significant difference between pre and post-treatment Modified Rankin Scales (MRS) (p<0.05) of all patients. First-line treatments were IVIg (n=19,44.2%), IVIg+steroid (n=20,46.5%), steroid(n=1,2.3%), IVIg+steroid+plasmapheresis(n=1,2.3%) and IVIg+plasmapheresis (n=1,%2.3). Second-line treatment was given to 7 (16.6%) patients (n=3,azathioprine; n=2,rituximab; n=1,azathioprine+rituximab; n=1,azathioprine+ micofenolate mofetil +methotrexate).The patients were separated in to two different groups according to first-line treatment modalities (group-1:only IVIg, group-2:IVIg+steroid). There was no difference between pre and post treatment MRS of both groups. Conclusion:This multicenter study showed that first-line immunotherapy modalities (IVIg versus IVIg+steroid) had equal efficacy for treatment CIDP patients in childhood.
Keywords: Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy, immunotherapy, IVIg, steroid
Gamze Sarıkaya Uzan
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Medicine, İzmir, Turkey
Turkey
Deniz Yüksel
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Dr Sami Ulus Maternity Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, University of
Turkey
Erhan Aksoy
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Dr Sami Ulus Maternity Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, University of
Turkey
Ülkühan Öztoprak
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Dr Sami Ulus Maternity Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, University of
Turkey
Mehmet Canpolat
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Selcan Öztürk
Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Çelebi Yıldırım
Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Ayten Güleç
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Hüseyin Per
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Objective:We aimed to evaluate the clinical, demographic, electrophysiological and treatment response of pediatric onset chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in Türkiye. Methods:The clinical data and electrophysiological results of patients with CIDP between January 2010-December 2021 from 14 centers were reviewed retrospectively. The patients were classified according to Joint Task Force of the European Federation Neurological of Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of CIDP (2021). Results:A total of 43 patients, 22 (%51.2) male and 21 (%48.8) female, were included in the study. The median age was 14.5 years (4.3-23) and the median age of onset of symptoms was 11 years (3 month-17 y). Thirty-eight patients were diagnosed with typical CIDP (88.4%) and 5 patients (11.6%) with possible CIDP. The most common electrophysiological finding of demyelination was ≥30 percent reduction of motor conduction velocity below the lower limit in two nerves (78.1%n= 25). All patients except one received immunotherapy either alone or in combination. There was a significant difference between pre and post-treatment Modified Rankin Scales (MRS) (p<0.05) of all patients. First-line treatments were IVIg (n=19,44.2%), IVIg+steroid (n=20,46.5%), steroid(n=1,2.3%), IVIg+steroid+plasmapheresis(n=1,2.3%) and IVIg+plasmapheresis (n=1,%2.3). Second-line treatment was given to 7 (16.6%) patients (n=3,azathioprine; n=2,rituximab; n=1,azathioprine+rituximab; n=1,azathioprine+ micofenolate mofetil +methotrexate).The patients were separated in to two different groups according to first-line treatment modalities (group-1:only IVIg, group-2:IVIg+steroid). There was no difference between pre and post treatment MRS of both groups. Conclusion:This multicenter study showed that first-line immunotherapy modalities (IVIg versus IVIg+steroid) had equal efficacy for treatment CIDP patients in childhood.
Keywords: Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy, immunotherapy, IVIg, steroid
Gamze Sarıkaya Uzan
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Medicine, İzmir, Turkey
Turkey
Deniz Yüksel
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Dr Sami Ulus Maternity Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, University of
Turkey
Erhan Aksoy
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Dr Sami Ulus Maternity Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, University of
Turkey
Ülkühan Öztoprak
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Dr Sami Ulus Maternity Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, University of
Turkey
Mehmet Canpolat
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Selcan Öztürk
Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Çelebi Yıldırım
Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Ayten Güleç
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Hüseyin Per
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
Turkey
Gamze Sarıkaya Uzan
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Medicine, İzmir, Turkey Turkey
Division of Child Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Medicine, İzmir, Turkey Turkey