Clinical Features Beyond Myopathy: Three Calpainopathy Patients with CAPN3 Mutation
Defne Alikılıç, Merve Öztürk, Adnan Deniz, Ömer Karaca, Mesut Güngör, Bülent Kara
OBJECTIVES We aimed to present the extramuscular clinical findings of 3 patients with the diagnosis of calpainopathy.
METHODS The data of the cases were obtained retrospectively from the pediatric neurology records of Kocaeli University Faculty of Medicine.
RESULTS
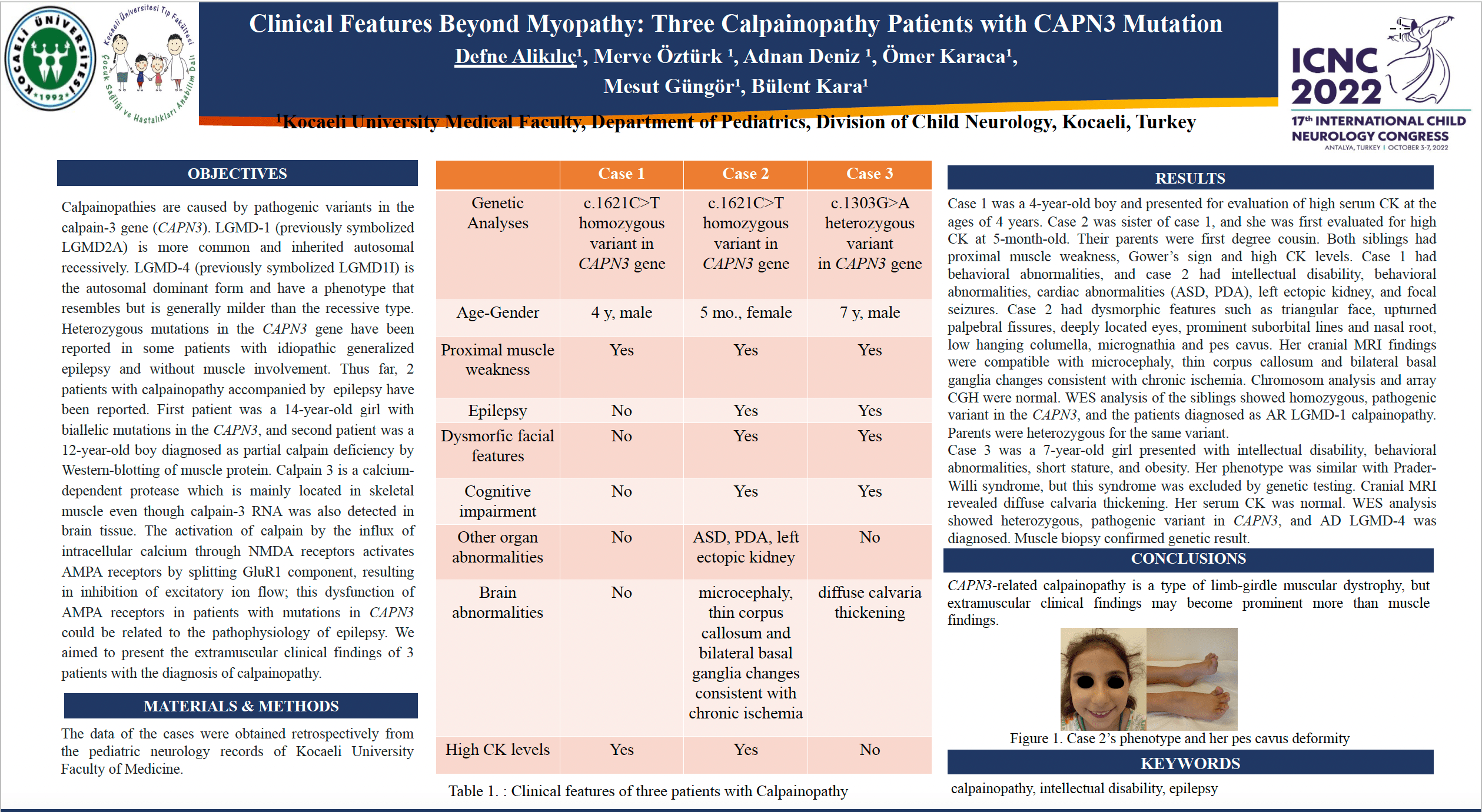
Case 1 was a 4-year-old boy and presented for evaluation of high serum CK at the ages of 4 years. Case 2 was sister of case 1, and she was first evaluated for high CK at 5-month-old. Their parents were first degree cousin. Both siblings had proximal muscle weakness, Gower’s sign and high CK levels. Case 1 had intellectual disability and behavioral abnormalities, and case 2 had intellectual disability, behavioral abnormalities, cardiac abnormalities (ASD, PDA), left ectopic kidney, and focal seizures. WES analysis of the siblings showed homozygous, pathogenic variant in the CAPN3, and the patients diagnosed as AR LGMD-1calpainopath. Parents were heterozygous for the same variant. Case 3 was a 7-year-old girl presented with intellectual disability, behavioral abnormalities, short stature, and obesity. Her phenotype was similar with Prader-Willi syndrome, but this syndrome was excluded by genetic testing. Cranial MRI revealed diffuse calvaria thickening without brain abnormalities. Her serum CK was normal. WES analysis showed heterozygous, pathogenic variant in CAPN3, and AD LGMD-4 was diagnosed. Muscle biopsy confirmed genetic result.
CONCLUSION CAPN3-related calpainopathy is a type of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, but exstramuscular clinical findings may become prominent more than muscle findings.
Keywords: calpainopathy, myopathy, epilepsy, intellectual disability
Defne Alikılıç
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Merve Öztürk
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Adnan Deniz
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Ömer Karaca
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Mesut Güngör
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Bülent Kara
Kocaeli University
Turkey
OBJECTIVES We aimed to present the extramuscular clinical findings of 3 patients with the diagnosis of calpainopathy.
METHODS The data of the cases were obtained retrospectively from the pediatric neurology records of Kocaeli University Faculty of Medicine.
RESULTS
Case 1 was a 4-year-old boy and presented for evaluation of high serum CK at the ages of 4 years. Case 2 was sister of case 1, and she was first evaluated for high CK at 5-month-old. Their parents were first degree cousin. Both siblings had proximal muscle weakness, Gower’s sign and high CK levels. Case 1 had intellectual disability and behavioral abnormalities, and case 2 had intellectual disability, behavioral abnormalities, cardiac abnormalities (ASD, PDA), left ectopic kidney, and focal seizures. WES analysis of the siblings showed homozygous, pathogenic variant in the CAPN3, and the patients diagnosed as AR LGMD-1calpainopath. Parents were heterozygous for the same variant. Case 3 was a 7-year-old girl presented with intellectual disability, behavioral abnormalities, short stature, and obesity. Her phenotype was similar with Prader-Willi syndrome, but this syndrome was excluded by genetic testing. Cranial MRI revealed diffuse calvaria thickening without brain abnormalities. Her serum CK was normal. WES analysis showed heterozygous, pathogenic variant in CAPN3, and AD LGMD-4 was diagnosed. Muscle biopsy confirmed genetic result.
CONCLUSION CAPN3-related calpainopathy is a type of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, but exstramuscular clinical findings may become prominent more than muscle findings.
Keywords: calpainopathy, myopathy, epilepsy, intellectual disability
Defne Alikılıç
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Merve Öztürk
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Adnan Deniz
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Ömer Karaca
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Mesut Güngör
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Bülent Kara
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Defne Alikılıç
Kocaeli University
Turkey
Kocaeli University
Turkey