Evaluation Of Neurodevelopmental Status Of Patients With Breath-Holding Spells(BHS) - Single Center Experience
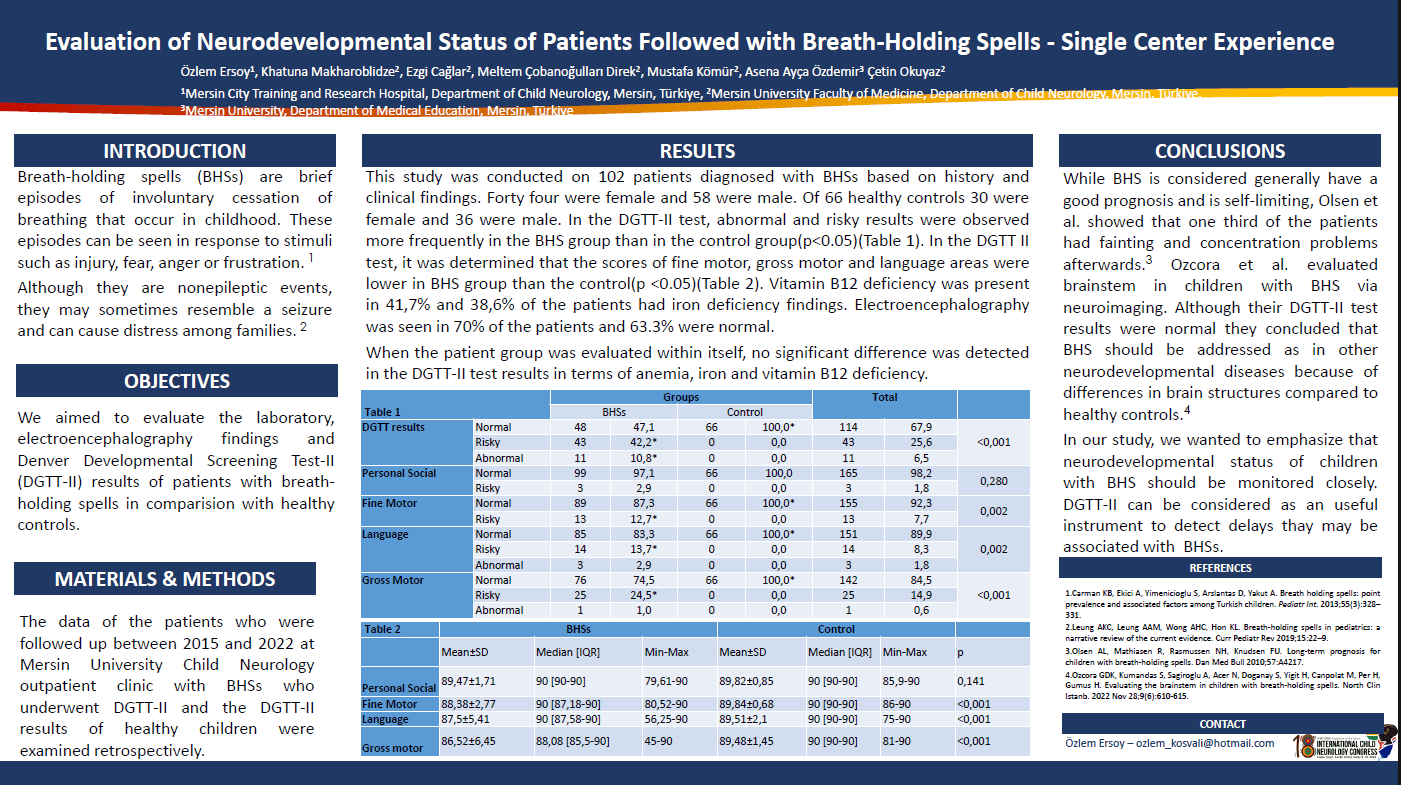
AIM: Evaluation of laboratory, electroencephalography findings and Denver Developmental Screening Test-II(DGTT-II) results of patients with BHS. METHOD: The data of the patients who were followed up between 2015 and 2022 at Mersin University Child Neurology outpatient clinic with BHS who underwent DGTT-II and the DGTT-II results of healthy children were examined retrospectively. RESULTS: Of the 102 patients diagnosed with BHS based on history and clinical findings, 44 were female.In the control group, 30 of the 66 patients were female. Anemia was detected in 19,8% of the patients. Vitamin B12 deficiency was present in 41,7% and 38,6% of the patients had iron deficiency findings. Electroencephalography was seen in 70% of the patients and 63.3% were normal. In the DGTT-II test, abnormal and risky results were observed more frequently in the BHS group than in the control group(p<0.05). In the DGTT II test, it was determined that the scores of fine motor, gross motor and language areas were lower in BHS group than the control(p <0.05). When the patient group was evaluated within itself, no significant difference was detected in the DGTT-II test results in terms of anemia, iron and vitamin B12 deficiency. CONCLUSION: BHS are non-epileptic paroxymal attacks that are common in childhood and may cause anxiety in families. In our study, we wanted to emphasize that the neurodevelopmental status of children with BHS should be monitored closely. DGTT-II test can be considered as an useful instrument to detect developmental delays that may be associated with BHS.
Özlem Ersoy
Turkey
Khatuna Makharoblidze
Turkey
Ezgi Çağlar
Turkey
Meltem Çobanoğulları Direk
Turkey
Mustafa Kömür
Turkey
Asena Ayça Özdemir
Turkey
Çetin Okuyaz
Turkey
Meltem Çobanoğulları Direk
Turkey