Genotype-Phenotype Spectrum Of Children With Epilepsy Undergoing Whole Exome Sequencing
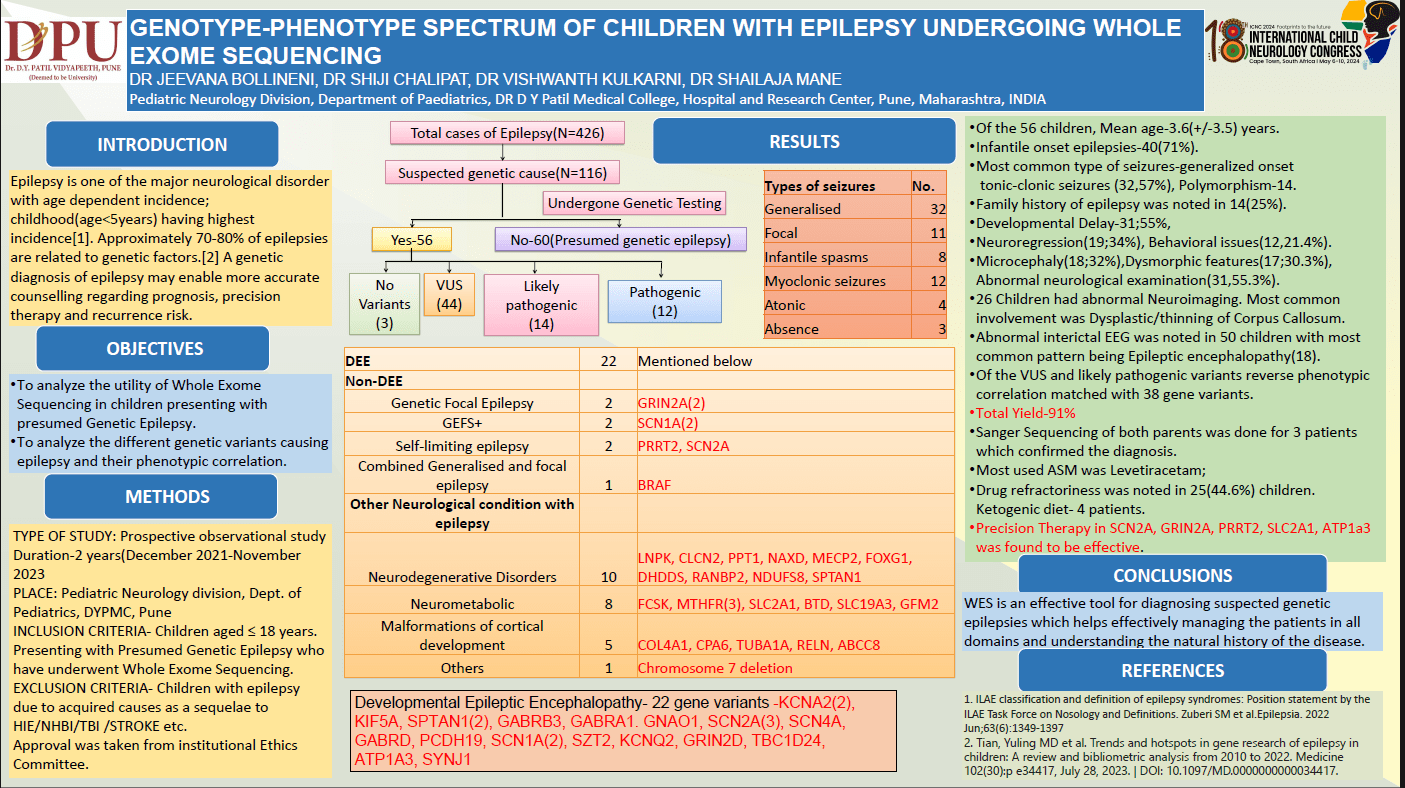
BACKGROUND: Approximately 30% of epilepsies have genetic aetiology. A genetic diagnosis of epilepsy may enable more accurate counselling regarding prognosis and recurrence risk, avoids unnecessary medical investigations and may change care. The main objective of this study is to describe the genes detected in our cohort and their phenotypic correlation and to investigate diagnostic utility of WES in paediatric epilepsies. METHODS: This is a prospective observational study conducted at a tertiary care centre in India over a period of two years (December 2021-November 2023). All children from birth to 18 years presenting with epilepsy were screened. Among them only 56 children of suspected genetic etiology and those who were affording WES were enrolled after an informed consent. Clinical profile, Electroencephalogram, radiological findings and WES reports were collected and results were analysed. RESULTS: Of the 56 children, 37(66%) had infantile onset epilepsy. Pathogenic or likely pathogenic genes were seen in 23(41.07%) children and 4 reports showed no detectable variants. A total 25 gene variants were described under the spectrum of Developmental Epileptic Encephalopathy. SCN1A is the most common gene in our cohort seen in 4(7.1%) children with variable expression followed by SCN2A(3;5.3%) and 2 each of GRIN2A, PCDH19 and CACNA1A gene variants. All the patients and relatives underwent a review of treatment, prognostication and possible prenatal genetic testing strategies were discussed. CONCLUSION: Whole Exome Sequencing is an effective tool for diagnosing suspected genetic epilepsy which helps effectively managing the patients in all domains and understanding the natural history of the disease.
Jeevana Bollineni
Dr D Y Patil medical college, hospital and research center
India
Shiji Chalipat
Dr D Y Patil Medical College
India
Vishwanath Kulkarni
Dr DY Patil Medical College
India
Jeevana Bollineni
Dr D Y Patil medical college, hospital and research center
India