Paroxysmal Non-epileptic Disorders Among Children And Adolescents In Ibadan, Nigeria
Background Paroxysmal non-epileptic disorders (PNEDs) are a heterogenous group of disorders characterized by clinical episodes similar to those of epileptic events but not accompanied by abnormal electrical discharges in the brain. These can be classified as physiological and psychogenic. They include movement disorders, sleep disorders, hypoxic ischaemic events, migraine associated disorders and psychogenic seizures. Few reports exist in Nigeria.
Aims To describe the incidence and clinical characteristics of PNEDs among children presenting at the Paediatric Neurology clinic of UCH, Ibadan.
Methods This was a retrospective cross-sectional study conducted at the Paediatric Neurology Clinic from December 2021 to October 2023. Children with a diagnosis of PNED who had been reviewed by the paediatric neurologists and confirmed by electroencephalography (EEG) were identified and clinical characteristics documented.
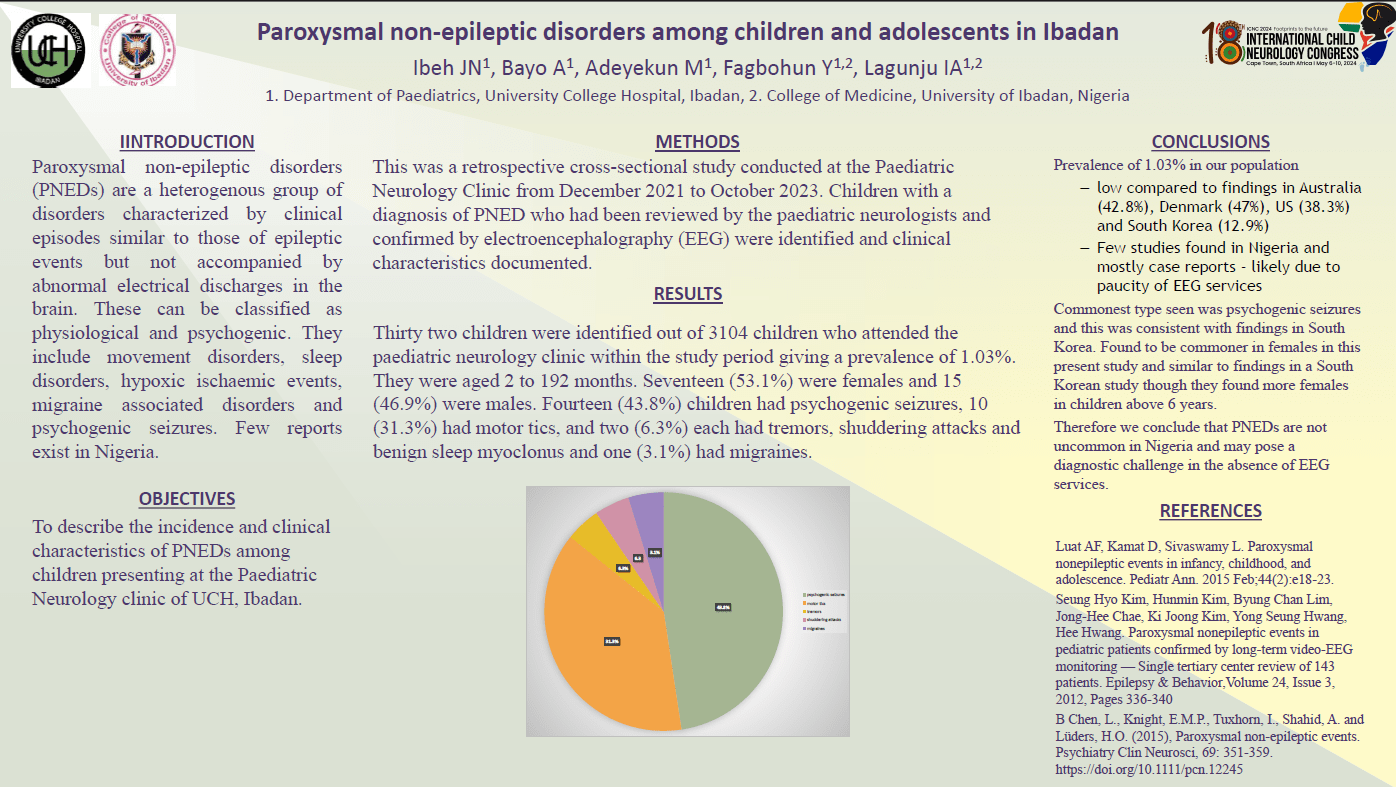
Results Thirty two children were identified out of 3104 children who attended the paediatric neurology clinic within the study period. They were aged 2 to 192 months. Seventeen (53.1%) were females and 15 (46.9%) were males. Fourteen (43.8%) children had psychogenic seizures, 10 (31.3%) had motor tics, and two (6.3%) each had tremors, shuddering attacks and benign sleep myoclonus and one (3.1%) had migraines.
Conclusion PNEDs are not uncommon in Nigeria and may pose a diagnostic challenge in the absence of EEG services.
Joy Ibeh
University College Hospital
Nigeria
Abieyuwa Fagbohun
University College Hospital
Nigeria
Joy Ibeh
University College Hospital
Nigeria