Epilepsy Care In Kenya: Gaps And Opportunities From Targeted Survey Of Health Workers
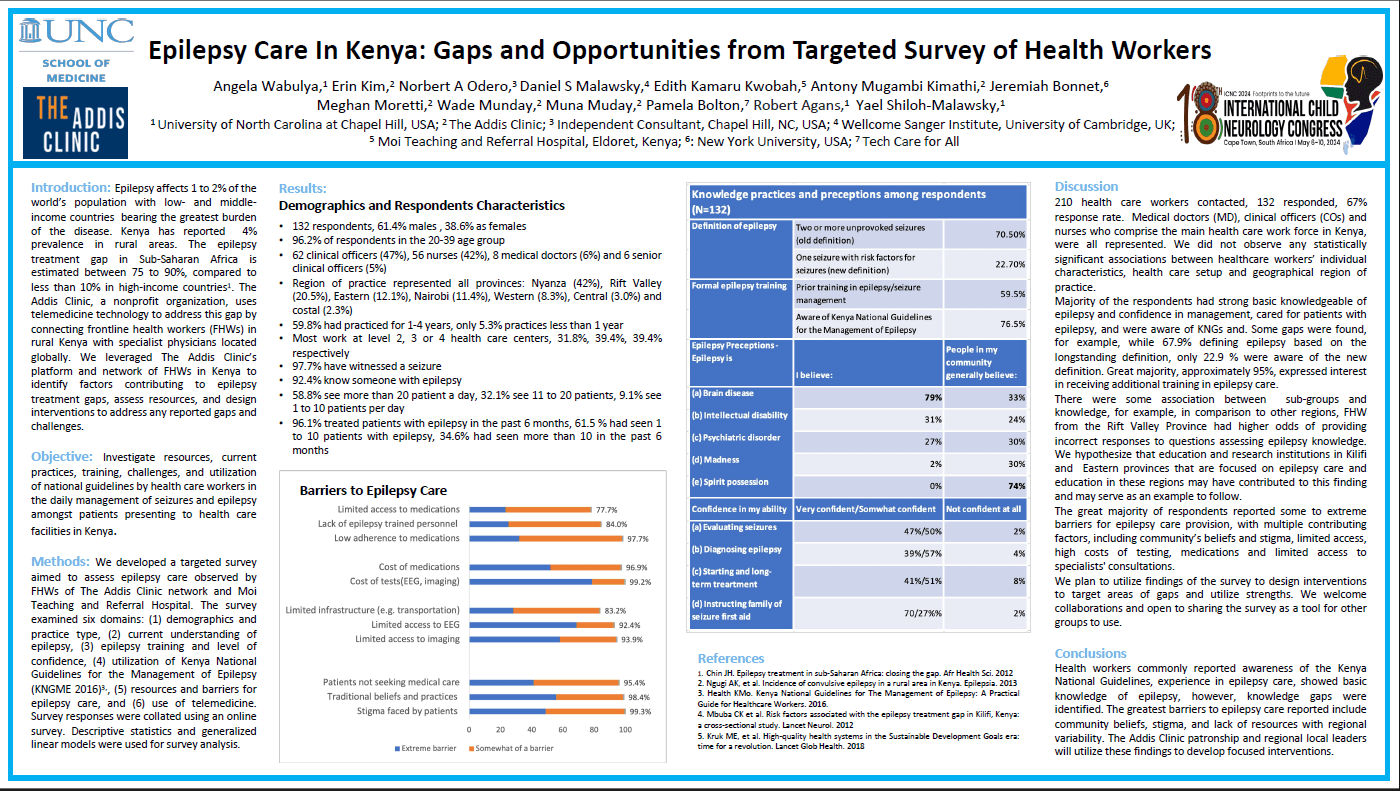
Objective: The epilepsy treatment gap in Sub-Saharan Africa is 75 to 90%, compared to less than 10% in high-income countries. The Addis Clinic uses telemedicine technology to connect frontline health workers in Kenya with specialist physicians. Epilepsy specialists hypothesized that The Addis Clinic platform and network of health workers in Kenya could be utilized to identify factors contributing to the epilepsy treatment gap and opportunities for intervention. Methods: Online survey of frontline health workers in The Addis Clinic network, and health professionals of Kanya’s Moi Teaching and Referral Hospital examined six domains: demographics and practice type, epilepsy understanding, formal training and confidence, utilization of Kenya National Guidelines, resources and barriers, and telemedicine use. Results: 210 health care workers contacted, survey response rate 62.9%. There were no statistically significant associations between healthcare workers’ characteristics, practice and region. Respondents were generally knowledgeable about epilepsy, some gaps of knowledge were found. About 60% reported receiving formal epilepsy training, 40% received post-graduation continued education. Over 95% expressed interest in further training. Majority of respondents reported some or extreme barriers to epilepsy care including community’s beliefs, stigma, limited access, costs of testing, medications, and specialists. Significance: Health workers commonly reported awareness of the Kenya National Guidelines, experience in epilepsy care, showed basic knowledge of epilepsy, however, knowledge gaps were identified. The greatest barriers to epilepsy care reported include community beliefs, stigma, and lack of resources with regional variability. The Addis Clinic patronship and regional local leaders will utilize these findings to develop focused interventions.
Yael Shiloh-Malawsky
University of North Carolina
United States
Angela Wabulya
University of North Carolina
United States
Norbert A Odero
United States
Daniel S Malawsky
University of Cambridge
United Kingdom
Edith Kamaru Kwobah
Moi Teaching and Referral Hospital
Kenya
Erin Kim
The Addis Clinic
United States
Antony Kimathi Mugambi
The Addis Clinic
Kenya
Meghan Moretti
The Addis Clinic
United States
Muna Muday
The Addis Clinic
United States
Pamela Bolton
Tech Care for All
United States
Robert Agans
University of North Carolina
United States
Yael Shiloh-Malawsky
University of North Carolina
United States