Intersection Of Social Disparity, Brain Injury And neurodevelopmental Outcomes In Children With Congenital Heart Disease
Children with congenital heart disease (CHD) have elevated risk for brain injury and neurodevelopmental impairments. Social disparity modifies the relationship between brain injury and neurodevelopment in preterm children. We assessed whether social disparity modified associations between brain injury and cognition in children with CHD.
We included a retrospective cohort of 245 children with CHD who underwent neonatal cardiac surgery with pre- or post-operative brain MRI. Moderate-severe brain injury included moderate-severe white matter injury, stroke, or grade 3-4 intraventricular hemorrhage. ON-Marg was used to assess social disparity, specifically material deprivation. Children were separated into 3 groups, Group 1 representing the least deprived and 3, the most deprived. 18-month cognitive outcomes were assessed with Bayley-3. Multivariable linear regression models were used to assess whether material deprivation modified associations between brain injury and cognition using an interaction term, adjusting for clinical confounders that were significantly associated with cognitive outcome in univariate regressions (p<0.05).
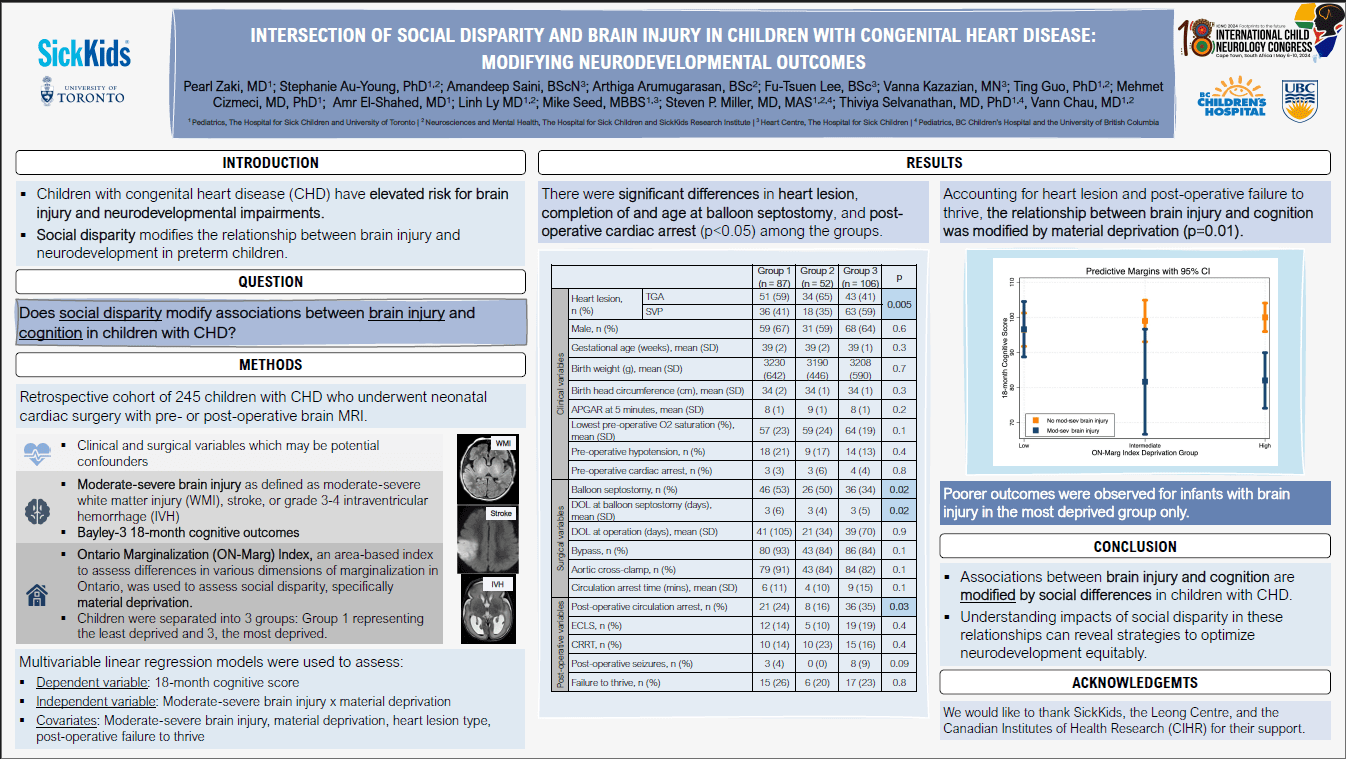
Among the groups, there were significant differences in heart lesion, completion of and age at balloon septostomy, and post-operative cardiac arrest (p<0.05). In the final regression model, accounting for heart lesion and post-operative failure to thrive, the relationship between brain injury and cognition was modified by material deprivation (p=0.01). Poorer outcomes were observed for infants with brain injury in the most deprived group only (Figure 2).
Associations between brain injury and cognition are modified by social differences in children with CHD. Understanding impacts of social disparity in these relationships can reveal strategies to optimize neurodevelopment equitably.
Disclosure: SickKids, Leong Centre.
Pearl Zaki
The Hospital for Sick Children and University of Toronto
Canada
Stephanie Au-Young
The Hospital for Sick Children
Canada
Amandeep Saini
The Hospital for Sick Children
Canada
Arthiga Arumugarasan
The Hospital for Sick Children
Canada
Fu-Tsuen Lee
The Hospital for Sick Children
Canada
Vanna Kazazian
The Hospital for Sick Children
Canada
Ting Guo
The Hospital for Sick Children
Canada
Mehmet Cizmeci
The Hospital for Sick Children and University of Toronto
Canada
Amr El-Shahed
The Hospital for Sick Children and University of Toronto
Canada
Linh Ly
The Hospital for Sick Children and University of Toronto
Canada
Mike Seed
The Hospital for Sick Children and University of Toronto
Canada
Steven Miller
BC Children’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia
Canada
Thiviya Selvanathan
BC Children’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia
Canada
Vann Chau
The Hospital for Sick Children and University of Toronto
Canada
Thiviya Selvanathan
BC Children’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia
Canada