Interaction Of Immune Response In Niemann Pick Disease Type C1 Of Children
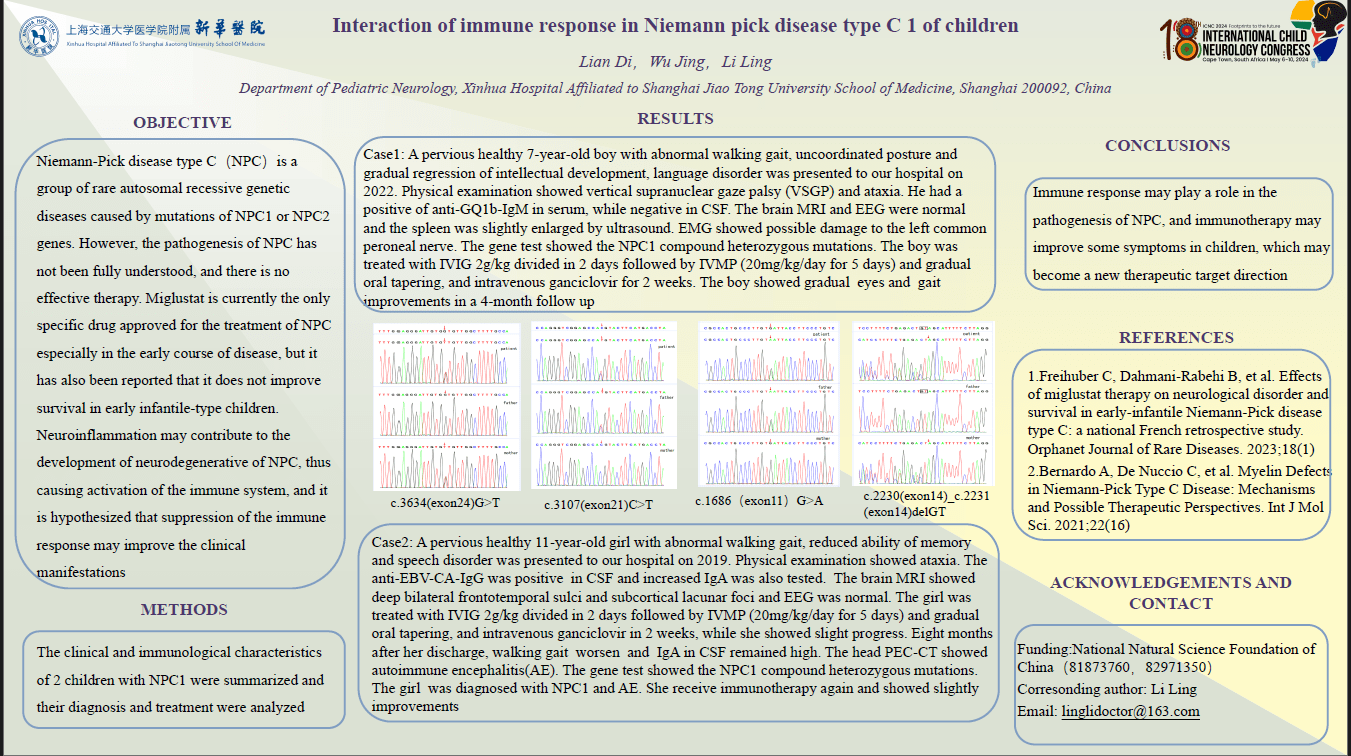
Objective: Niemann-Pick disease type C,(NPC)is a group of rare autosomal recessive genetic diseases caused by mutations of NPC1 and NPC2 genes, in which unesterified cholesterol and glycosphingolipdis are accumulated in endosomes and lysosomes. However, the pathogenesis of NPC has not been fully understood, and there is no effective cure. The clinical management is mainly symptomatic and supportive. Neuroinflammation may contribute to the development of neurodegenerative of NPC, thus causing activation of the immune system, and it is hypothesized that suppression of the immune response may improve the clinical manifestations.Methods: The clinical and immunological characteristics of 2 children with NPC1 were summarized and their diagnosis and treatment were analyzed. Results: Both of the 2 children with NPC1 were not diagnosed at the early stage of the disease , and the time between onset and diagnosis lasted for about 2 years. 1 case was combined with persistently elevated cerebrospinal fluid IgA, and the other case was combined with positive serum anti-GQ1b antibody, while immunotherapy improved the symptoms of both cases to different degrees.Conclusion:Immune response may play a role in the pathogenesis of NPC, and immunotherapy may improve some symptoms in children, which may become a new therapeutic target direction.
Di Lian
Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
China
Jing Wu
Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
China
Ling Li
Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
China
Ling Li
Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
China