Higher Economic Burden Of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) Compared To Other Chronic Diseases
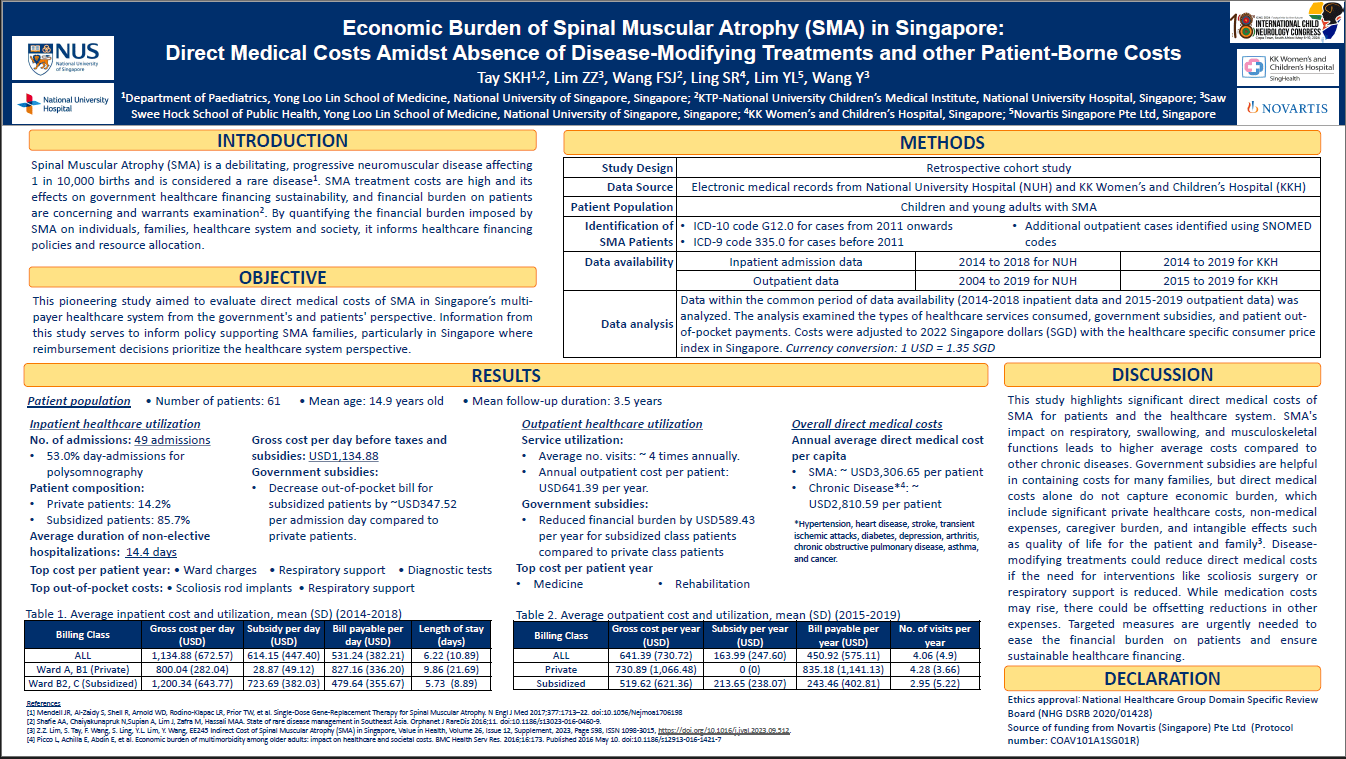
Introduction The Singapore Orphan Drug Act regulates access to medicines for diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) but there is no specific governmental funding for SMA treatments. This study aimed to evaluate direct medical costs of SMA in Singapore’s multi-payer healthcare system. Methods Retrospective electronic data were extracted from two major hospitals between January 2004 and December 2019 treating SMA. Analysis examined the types of healthcare services consumed, government subsidies and patient out-of-pocket payments. Costs were adjusted to 2022 Singapore dollars (SGD). Annual cost per capita are compared to cost of chronic conditions including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory disorders. Results Sixty-one patients were identified via ICD and SNOMED codes. Amongst 54 admissions, 49.1% were day-admissions for polysomnography. Average non-elective hospitalization duration was 14.4 days, costing SGD$1553.93/day. Patients sought outpatient services approximately four times annually, incurring roughly SGD865.87/year. Where applicable, government assistance reduced payments by SGD$448.57 per inpatient admission day and by SGD$911.83 per outpatient year. Scoliosis rod implants and respiratory support were the largest inpatient costs while medications and rehabilitation the largest outpatient costs. Annual direct healthcare cost per capita for SMA is approximately SGD4068.40, compared to SGD3794.29 for a patient with chronic disease. Conclusion This study highlights the significant medical costs and healthcare utilization patterns of SMA in Singapore. While medication cost is projected to increase with disease-modifying treatments, there may be corresponding reduction in other costs. There remains an urgent need for targeted measures to alleviate financial burden on patients and ensure sustainability of healthcare financing.
Stacey Tay
National University of Singapore
Singapore
Zhi Zhen Lim
National University of Singapore
Singapore
Furene Wang
National University Health System
Singapore
Simon Ling
KK Women's and CHildren's Hospital
Singapore
Yan Ling Lim
Novartis Singapore Pte Ltd
Singapore
Yi Wang
National University of Singapore
Singapore